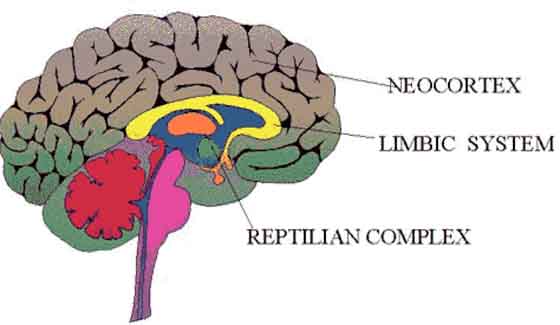

The triune brain is a model of the evolution of the vertebrate forebrain and behavior, proposed by the American physician and neuroscientist Paul D. MacLean. MacLean originally formulated his model in the 1960s and propounded it at length in his 1990 book The Triune Brain in Evolution.
The triune brain consists of the reptilian complex, the paleomammalian complex (limbic system), and the neomammalian complex (neocortex), viewed as structures sequentially added to the forebrain in the course of evolution. However, this hypothesis is no longer espoused by the majority of comparative neuroscientists in the post-2000 era.
The triune brain hypothesis became familiar to a broad popular audience through Carl Sagan's Pulitzer prize winning 1977 book The Dragons of Eden. The theory has been embraced by some psychiatrists and at least one leading affective neuroscience researcher.
The reptilian complex, also known as the R-complex or "reptilian brain" was the name MacLean gave to the basal ganglia, structures derived from the floor of the forebrain during development. The term derives from the idea that comparative neuroanatomists once believed that the forebrains of reptiles and birds were dominated by these structures. MacLean proposed that the reptilian complex was responsible for species-typical instinctual behaviors involved in aggression, dominance, territoriality, and ritual displays. Read more

Reptilian Gods Create Bloodlines and a Biogenetic Experiment Called Humans
Release of Information from the 8 Origin Cells at the Base of the Spine
Spiraling DNA, Golden Ratio, Fibonacci Numbers, Consciousness