The TV series "Fringe" featured a blue seahorse glyph.
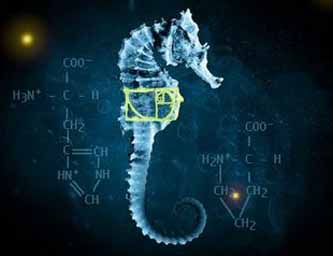
The Fringe Seahorse glyph has the Fibonacci spiral on its side, the spiral itself is contained inside a visual representation of the golden ratio. Its tail is also a Fibonacci spiral. Some images also include stick diagrams for the amino acids L-histidine and L-proline. The seahorse is featured in the season 2 episode "The Bishop Revival" in which it's revealed that Walter Bishop's father was nicknamed Seahorse, he signed his chemical with a seahorse. The number "6" is prominently featured within the center of the seahorse three times.. 666, the mark of the beast or the devil, has been hidden in the seahorse.
The seahorse can be seen briefly flashed in the title sequence during the molecular zoom portion. In the center of the of the seahorse, there is the graph of the Golden Ratio, in which is the Fibonacci Spiral. The Greek letter Phi is used to symbolize the Golden Ratio and is the same Greek letter seen in the Frog Glyph.
The brain region widely believed to be responsible for memory consolidation, behavioral inhibition, and spatial mapping is called the hippocampus, which is Latin for seahorse. Walter Bishop has three regions of his hippocampus surgically removed (Grey Matters) and loses selective memories. Walter's memory difficulties, impulsivity, and other odd behaviors are likely due to these hippocampal lesions.

Seahorse (also written sea-horse and sea horse) is the name given to 45 species of small marine fishes in the genus Hippocampus. "Hippocampus" comes from the Ancient Greek hippokampos meaning "horse" and kampos meaning "sea monster". Having a head and neck suggestive of a horse, seahorses also feature segmented bony armor, an upright posture and a curled prehensile tail. Read more
The Ancient Greeks and Romans believed the seahorse was an attribute of the sea god Neptune/Poseidon and as such, the seahorse was considered a symbol of strength and power.
Ancient Europeans believed that the seahorse carried the souls of deceased sailors to the underworld - giving them safe passage and protection until the met their destination/destiny.
Chinese cultures believed that the seahorse was a type of sea dragon, and as such they were revered for their power and thought to be symbols of good luck. Sailors have long viewed the seahorse as a good luck charm too.
The symbolic meaning of seahorse is quite intricate and diverse as this little creature itself is full of surprises. The seahorse is quite a unique creature, and thought to have mystical significance among the Ancient Greeks, European (alchemists) and Asians.
Symbolic meaning of Seahorses carry the following significances: Patience, Friendliness, Protection, Inflexibility, Perspective, Generosity/Sharing, High-Perception, Persistence, and Contentment. A relatively calm, and mild-mannered creature, the seahorse is seemingly content to roam the seas. Their bodies are geared for ambling-type motion - not for speed. Thus, they are symbolic of patience and contentment - they are happy with being where they are, and are in no hurry for advancement.
Further testimony to these attributes is the lack of evolution of the seahorse's body style. They have remained with this body style without change since their inception. Content to be who they are, and not feeling the need to change - these are a few profound lessons the seahorse provides us. However, along with a resistance to change, and a carefree approach to progress, the seahorse can be a symbol of inflexibility or stubbornness. To wit, the seahorse wraps its tail around the nearest object in order to anchor itself in turbulent waters. This is a lesson to be persistent in our goals, but be mindful that we are not too inflexible or stubborn in our achieving them.
A unique aspect of the seahorse is that the male is impregnated by the female and carries the offspring to term. This is a message of sharing the load in the home, and gaining perspective of both sides (genders) of an argument or situation. The seahorse has a boney exoskeleton which is a message of protection. Often when the seahorse comes to us it is a sign that we either need protection from our external circumstances, or we are building walls that aren't needed. Their armor-bodies are a sign that sometimes we might need to let our guard down - or perhaps we are leaving too open to get hurt.
Fragile seashores were the cradle of evolution for early fish around 420 million years ago not coral reefs as previously thought, fossils reveal Daily Mail - October 25, 2018
Fragile seashores were the 'cradle of evolution' for the first fish - not coral reefs as previously thought, according to new research.
A new study suggests fish originated in shallow ocean waters - such as lagoons - some 480 to 360 million years ago before diversifying into deeper waters, rivers and even on to land. The first vertebrates on Earth were fish that appeared around 480 million years ago but fossil records from this time are sparse with only small fragments identified. By 420 million years ago, there was a proliferation in the fossil record with a huge variety of fish species present en masse.
The galloping evolution in seahorses Science Daily - December 14, 2016
Without a doubt, the seahorse belongs to Darwin's "endless forms most beautiful." Its body form is one of a kind. It has neither a tail nor pelvic fin, it swims vertically, bony plates reinforce its entire body and it has no teeth, a rare feature in fish. Another peculiarity is that male seahorses are the ones to become pregnant. The genome project, comprising six evolutionary biologists from Professor Axel Meyer's research team from Konstanz and researchers from China and Singapore, sequenced and analyzed the genome of the tiger tail seahorse. They obtained new molecular evolutionary results that are relevant for biodiversity research: the loss and duplication of genes as well as the loss of regulative elements in its genome have both contributed to the rapid evolution of the seahorse.
 Seahorses stalk their prey by stealth BBC - November 27, 2013
Seahorses stalk their prey by stealth BBC - November 27, 2013
Seahorses may appear slow and awkward but they are ferocious and ingenious predators, according to a new study. The beautiful creatures are famously bad swimmers, but they have a secret weapon to sneak up on their prey. Their peculiar snouts are shaped to create very few ripples in the water, effectively cloaking them as they creep up and pounce on tiny crustaceans. The seahorse is one the slowest swimming fish we know of, but it's able to capture prey that swim at incredible speeds.
Why Seahorses Are Shaped Like Horses Scientific American - November 26, 2013
The seahorse head's shape helps the fish stealthily ambush prey, researchers say. Seahorses are unique among fish for having bent necks and long-snouted heads that make them resemble horses. The overall shape of their body, including the lack of a tail fin, helps make them "one of the slowest swimmers on the planet. They don't swim very much - they tend to anchor themselves to surfaces like seagrass with their prehensile tails.
Secret of the Sea Horse: How Creature Got its Curve Live Science - January 25, 2011
To understand how the seahorse's peculiar head, neck and trunk might have evolved, scientists analyzed how effective the animals were at capturing food when compared with pipefish. If a horselike shape provided the ancestors of sea horses an edge when it came to finding a meal, that could help explain why it developed, the investigators reasoned. Computer simulations revealed the shape and posture of sea horses helped them pivot forward to capture prey. High-speed video footage of both sea horses and pipefish corroborated these findings, revealing that sea horses can strike farther than pipefish. The curved bodies of sea horses would therefore enlarge the area they could probe for prey. This is especially useful for sit-and-wait predators such as sea horses, which often hide amid coral or sea grass, holding themselves in place with their prehensile, or grasping, tails.
Ancient Pygmy Pipehorse Species Found - National Geographic - May 10, 2012
Fossils of a new species of pygmy pipehorse - a relative of the seahorse - have been discovered in Slovenia, a new study says. Scientists discovered the 1-inch-long (2.5-centimeter-long) species dubbed Hippotropiscis frenki in a fossil-rich region called the Tunjice Hills, where the team also found the oldest known seahorse fossils in 2009. Pygmy pipehorses are thought to be an evolutionary link between seahorses and their close relatives, including pipefish and seadragons.
