
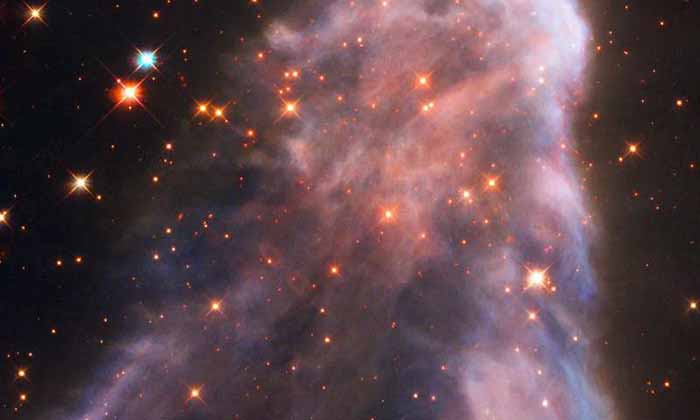
NASA Reveals Spooky Eyes in Space, And They're Staring Straight at You
Composite image combining Hubble and JWST data
Science Alert - November 1, 2024

NASA Reveals Spooky Eyes in Space, And They're Staring Straight at You
Composite image combining Hubble and JWST data
Science Alert - November 1, 2024

Rigel and the Witch Head Nebula APOD - October 31, 2024
Explanation: By starlight, this eerie visage shines in the dark with a crooked profile evoking its popular name, the Witch Head Nebula. In fact, this entrancing telescopic portrait gives the impression that a witch has fixed her gaze on Orion's bright supergiant star Rigel. More formally known as IC 2118, the Witch Head Nebula spans about 50 light-years and is composed of interstellar dust grains reflecting Rigel's starlight. The color of the Witch Head Nebula is caused not only by Rigel's intense blue light, but because the dust grains scatter blue light more efficiently than red. The same physical process causes Earth's daytime sky to appear blue, although the scatterers in Earth's atmosphere are molecules of nitrogen and oxygen. Rigel and this dusty cosmic crone are about 800 light-years away. You may still see a few witches in your neighborhood tonight though, so have a safe and Happy Halloween!

LDN 43: The Cosmic Bat Nebula APOD - October 27, 2024
Explanation: What is the most spook-tacular nebula in the galaxy? One contender is LDN 43, which bears an astonishing resemblance to a vast cosmic bat flying amongst the stars on a dark Halloween night. Located about 1400 light years away in the constellation Ophiuchus, this molecular cloud is dense enough to block light not only from background stars, but from wisps of gas lit up by the nearby reflection nebula LBN 7. Far from being a harbinger of death, this 12-light year-long filament of gas and dust is actually a stellar nursery. Glowing with eerie light, the bat is lit up from inside by dense gaseous knots that have just formed young stars.

Phantoms in Cassiopeia APOD - October 26, 2024
Explanation: These brightly outlined flowing shapes look ghostly on a cosmic scale. A telescopic view toward the constellation Cassiopeia, the colorful skyscape features the swept-back, comet-shaped clouds IC 59 (left) and IC 63. About 600 light-years distant, the clouds aren't actually ghosts. They are slowly disappearing though, under the influence of energetic radiation from hot, luminous star gamma Cas. Gamma Cas is physically located only 3 to 4 light-years from the nebulae and lies just above the right edge of the frame. Slightly closer to gamma Cas, IC 63 is dominated by red H-alpha light emitted as hydrogen atoms ionized by the hot star's ultraviolet radiation recombine with electrons. Farther from the star, IC 59 shows less H-alpha emission but more of the characteristic blue tint of dust reflected star light. The field of view spans over 1 degree or 10 light-years at the estimated distance of the interstellar apparitions.

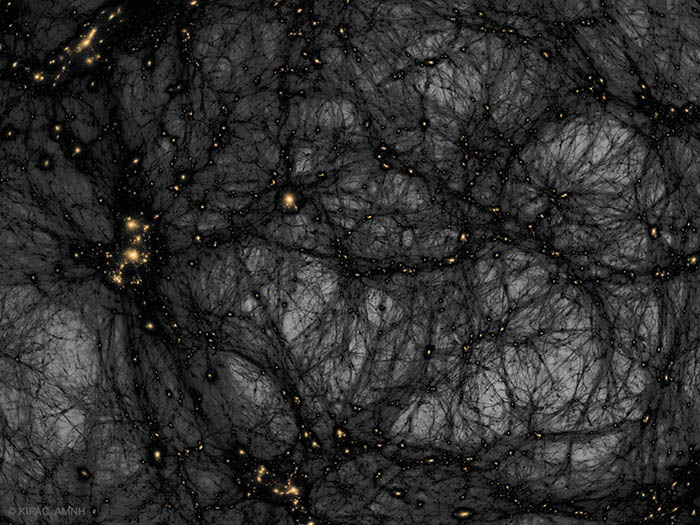
Dark Matter in a Simulated Universe APOD - October 20, 2024
Is our universe haunted? It might look that way on this dark matter map. The gravity of unseen dark matter is the leading explanation for why galaxies rotate so fast, why galaxies orbit clusters so fast, why gravitational lenses so strongly deflect light, and why visible matter is distributed as it is both in the local universe and on the cosmic microwave background. The featured image from the American Museum of Natural History's Hayden Planetarium Space Show Dark Universe highlights one example of how pervasive dark matter might haunt our universe. In this frame from a detailed computer simulation, complex filaments of dark matter, shown in black, are strewn about the universe like spider webs, while the relatively rare clumps of familiar baryonic matter are colored orange. These simulations are good statistical matches to astronomical observations. In what is perhaps a scarier turn of events, dark matter - although quite strange and in an unknown form - is no longer thought to be the strangest source of gravity in the universe. That honor now falls to dark energy, a more uniform source of repulsive gravity that seems to now dominate the expansion of the entire universe.
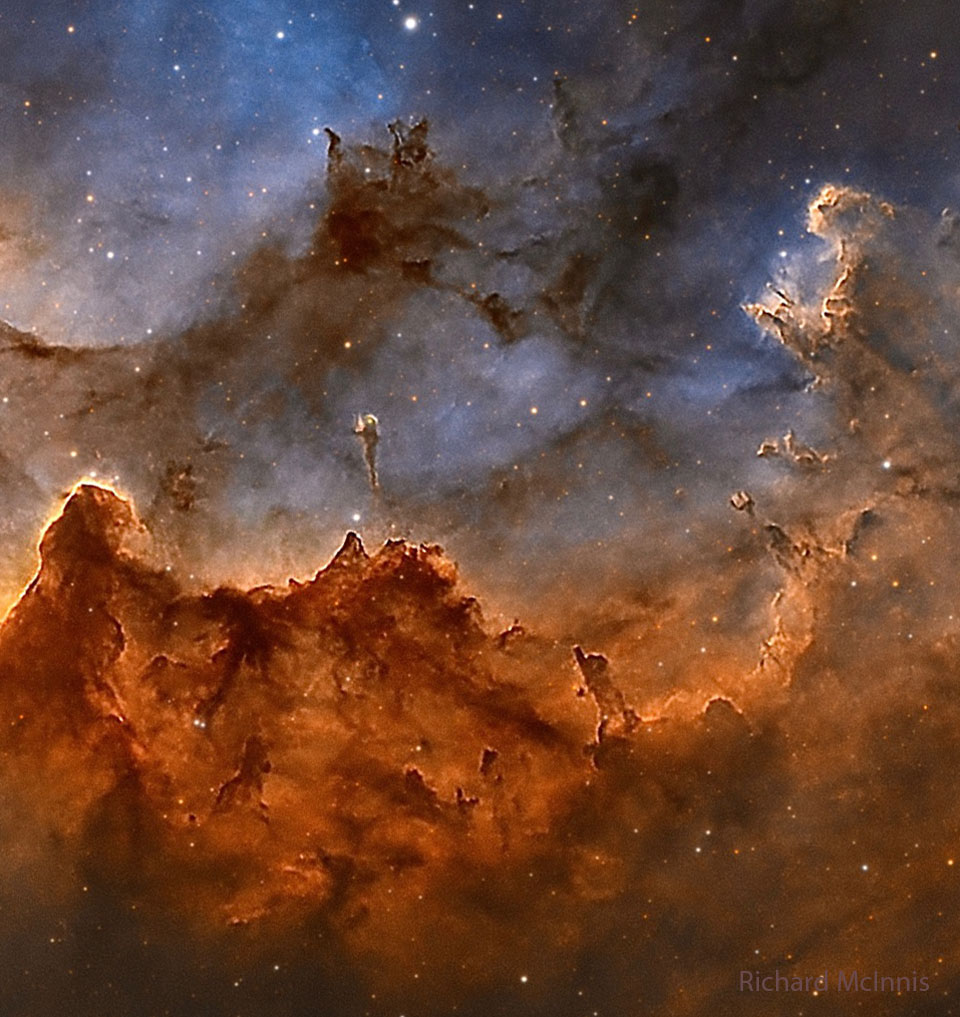

Halloween and the Wizard Nebula APOD - October 31, 2023
Explanation: Halloween's origin is ancient and astronomical. Since the fifth century BC, Halloween has been celebrated as a cross-quarter day, a day halfway between an equinox (equal day / equal night) and a solstice (minimum day / maximum night in the northern hemisphere). With a modern calendar however, even though Halloween occurs today, the real cross-quarter day will occur next week. Another cross-quarter day is Groundhog Day. Halloween's modern celebration retains historic roots in dressing to scare away the spirits of the dead. Perhaps a fitting tribute to this ancient holiday is this closeup view of the Wizard Nebula (NGC 7380). Visually, the interplay of stars, gas, and dust has created a shape that appears to some like a fictional ancient sorcerer. Although the nebula may last only a few million years, some of the stars being conjured from the gas by the great gravitational powers may outlive our Sun.
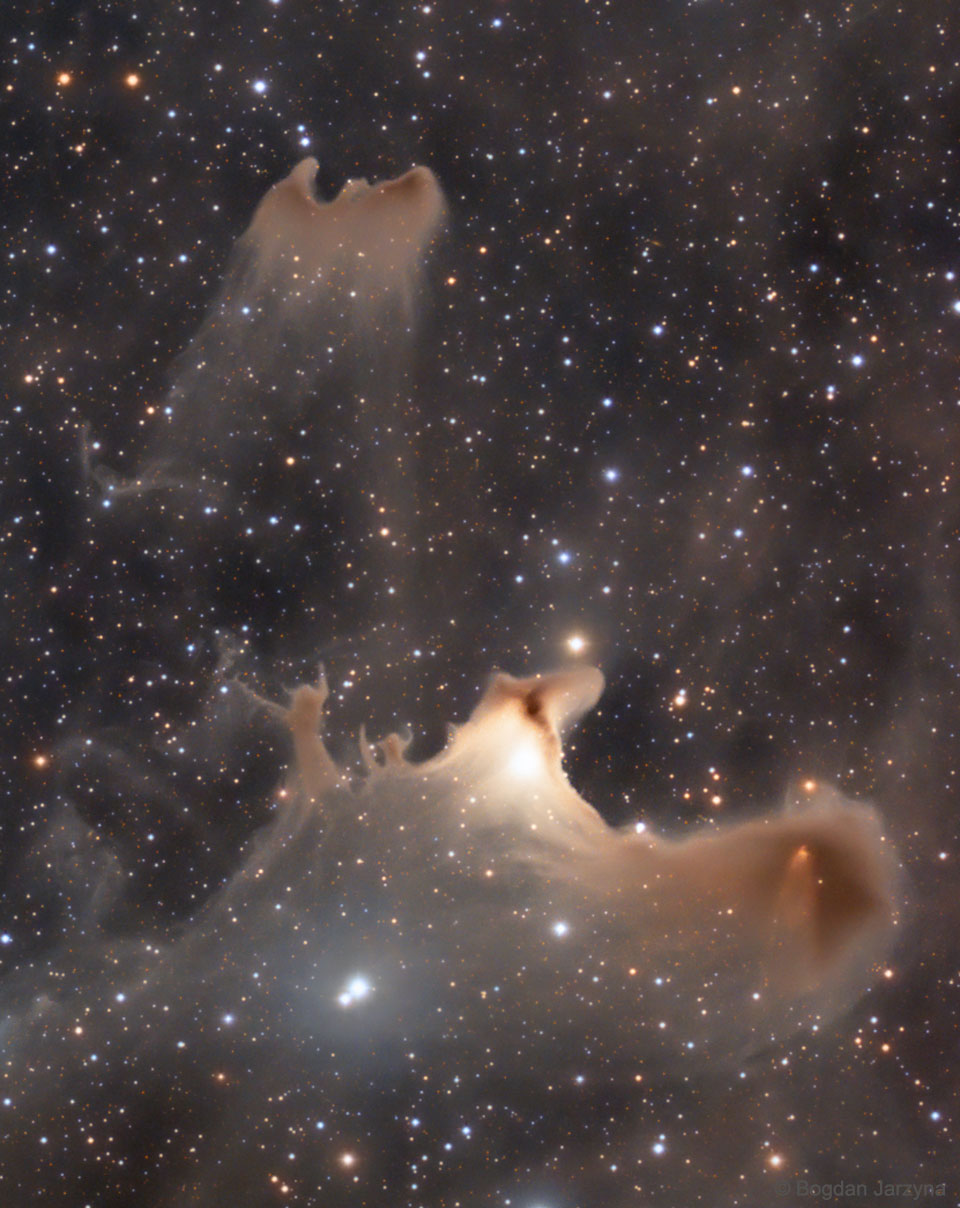

Reflections of the Ghost Nebula NASA - October 30, 2023
Explanation: Do any shapes seem to jump out at you from this interstellar field of stars and dust? The jeweled expanse, filled with faint, starlight-reflecting clouds, drifts through the night in the royal constellation of Cepheus. Far from your own neighborhood on planet Earth, these ghostly apparitions lurk along the plane of the Milky Way at the edge of the Cepheus Flare molecular cloud complex some 1,200 light-years away. Over two light-years across and brighter than the other spooky chimeras, VdB 141 or Sh2-136 is also known as the Ghost Nebula, seen toward the bottom of the featured image. Within the reflection nebula are the telltale signs of dense cores collapsing in the early stages of star formation.
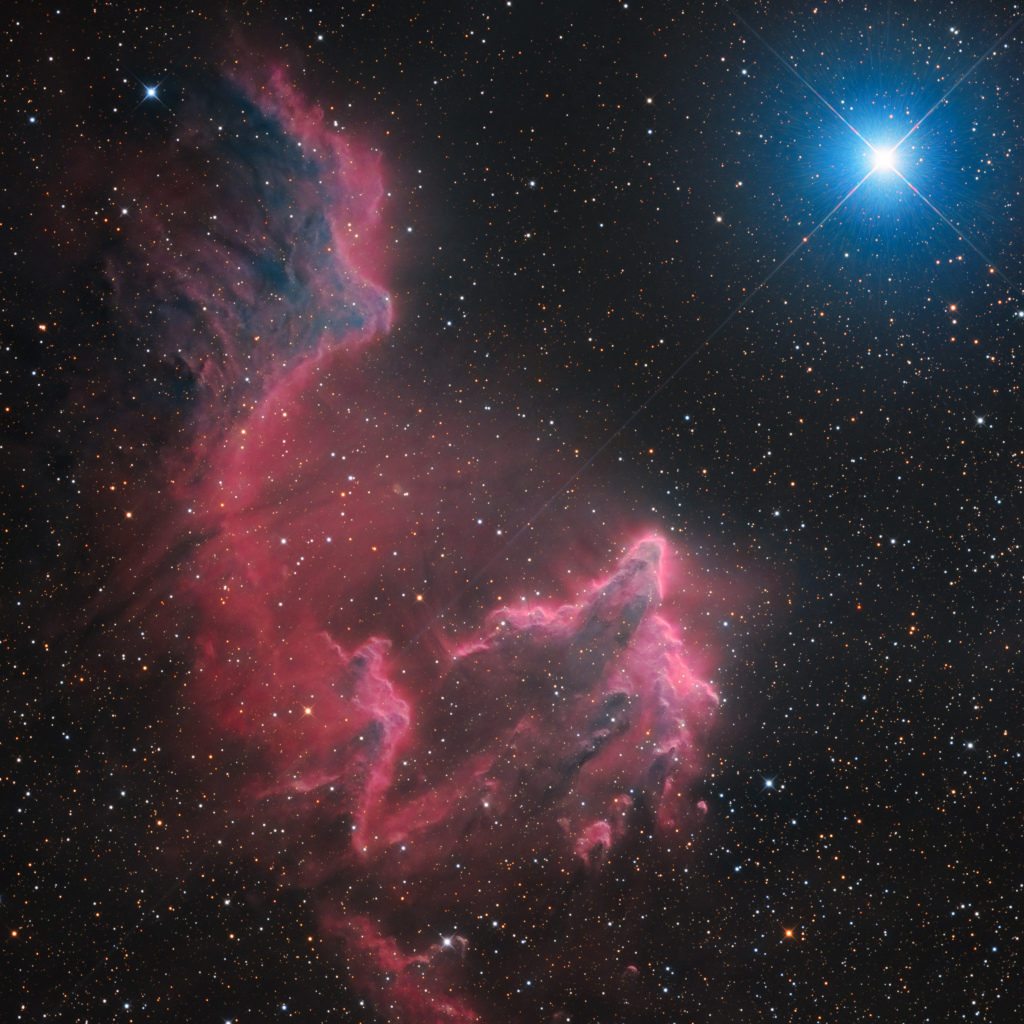

The Ghosts of Gamma Cas NASA - October 28, 2023
Explanation: Gamma Cassiopeiae shines high in northern autumn evening skies. It's the brightest spiky star in this telescopic field of view toward the constellation Cassiopeia. Gamma Cas shares the ethereal-looking scene with ghostly interstellar clouds of gas and dust, IC 59 (top left) and IC 63. About 600 light-years distant, the clouds aren't actually ghosts. They are slowly disappearing though, eroding under the influence of energetic radiation from hot and luminous gamma Cas. Gamma Cas is physically located only 3 to 4 light-years from the nebulae. Slightly closer to gamma Cas, IC 63 is dominated by red H-alpha light emitted as hydrogen atoms ionized by the star's ultraviolet radiation recombine with electrons. Farther from the star, IC 59 shows proportionally less H-alpha emission but more of the characteristic blue tint of dust reflected star light. The cosmic stage spans over 1 degree or 10 light-years at the estimated distance of gamma Cas and friends.
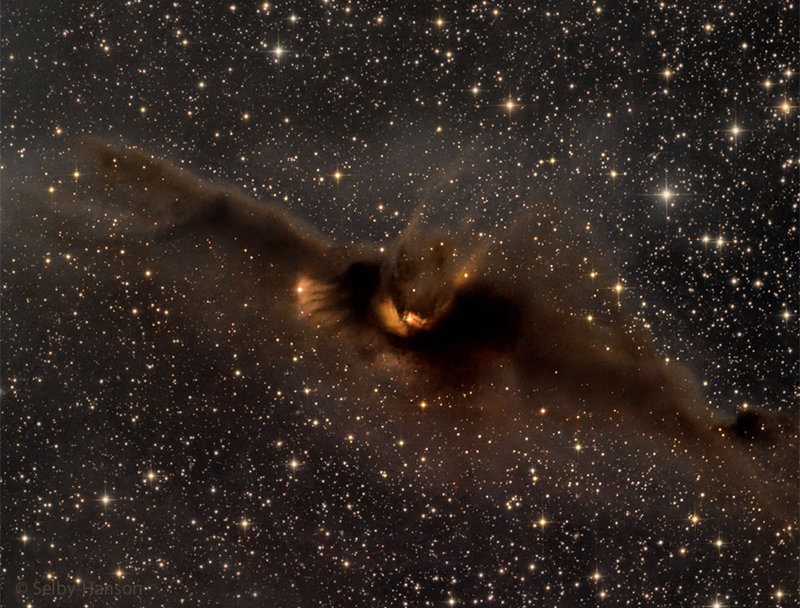

The Cosmic Bat Nebula NASA - October 31, 2022
Explanation: What is the most spook-tacular nebula in the galaxy? One contender is LDN 43, which bears an astonishing resemblance to a vast cosmic bat flying amongst the stars on a dark Halloween night. Located about 1400 light years away in the constellation Ophiuchus, this molecular cloud is dense enough to block light not only from background stars, but from wisps of gas lit up by the nearby reflection nebula LBN 7. Far from being a harbinger of death, this 12-light year-long filament of gas and dust is actually a stellar nursery. Glowing with eerie light, the bat is lit up from inside by dense gaseous knots that have just formed young stars.
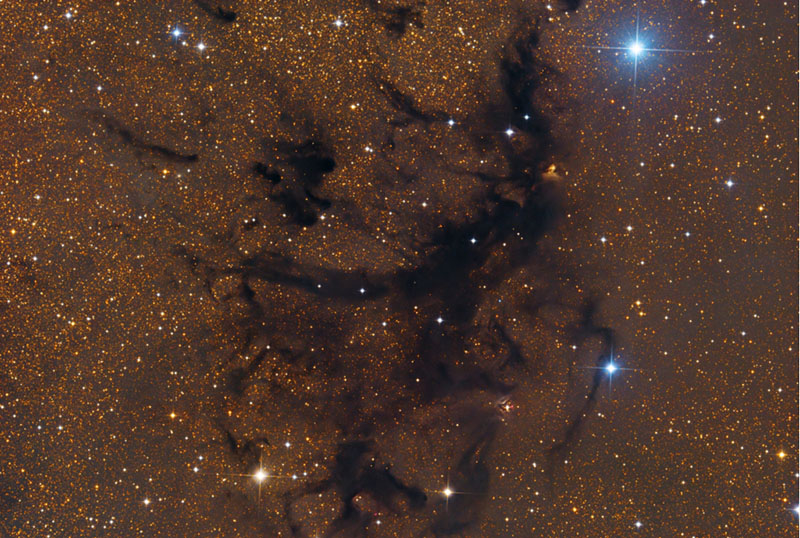

Dark Clouds in Aquila NASA - October 29, 2022
Explanation: Part of a dark expanse that splits the crowded plane of our Milky Way galaxy, the Aquila Rift arcs through planet Earth's skies near bright star Altair. In eerie silhouette against the Milky Way's faint starlight, its dusty molecular clouds likely contain raw material to form hundreds of thousands of stars and astronomers search the dark clouds for telltale signs of star birth. This telescopic close-up looks toward the region at a fragmented Aquila dark cloud complex identified as LDN 673, stretching across a field of view slightly wider than the full moon. In the scene, visible indications of energetic outflows associated with young stars include the small red tinted nebulosity RNO 109 above and right of center, and Herbig-Haro object HH32 below. These dark clouds might look scary, but they're estimated to be some 600 light-years away. At that distance, this field of view spans about 7 light-years.
NASA Spotted The Sun Smiling Science Alert - October 29, 2022
Dark Matter in a Simulated Universe NASA - October 31, 2021
Explanation: Is our universe haunted? It might look that way on this dark matter map. The gravity of unseen dark matter is the leading explanation for why galaxies rotate so fast, why galaxies orbit clusters so fast, why gravitational lenses so strongly deflect light, and why visible matter is distributed as it is both in the local universe and on the cosmic microwave background. The featured image from the American Museum of Natural History's Hayden Planetarium Space Show Dark Universe highlights one example of how pervasive dark matter might haunt our universe. In this frame from a detailed computer simulation, complex filaments of dark matter, shown in black, are strewn about the universe like spider webs, while the relatively rare clumps of familiar baryonic matter are colored orange. These simulations are good statistical matches to astronomical observations. In what is perhaps a scarier turn of events, dark matter - although quite strange and in an unknown form - is no longer thought to be the strangest source of gravity in the universe. That honor now falls to dark energy, a more uniform source of repulsive gravity that seems to now dominate the expansion of the entire universe. - Tom Abel & Ralf Kaehler
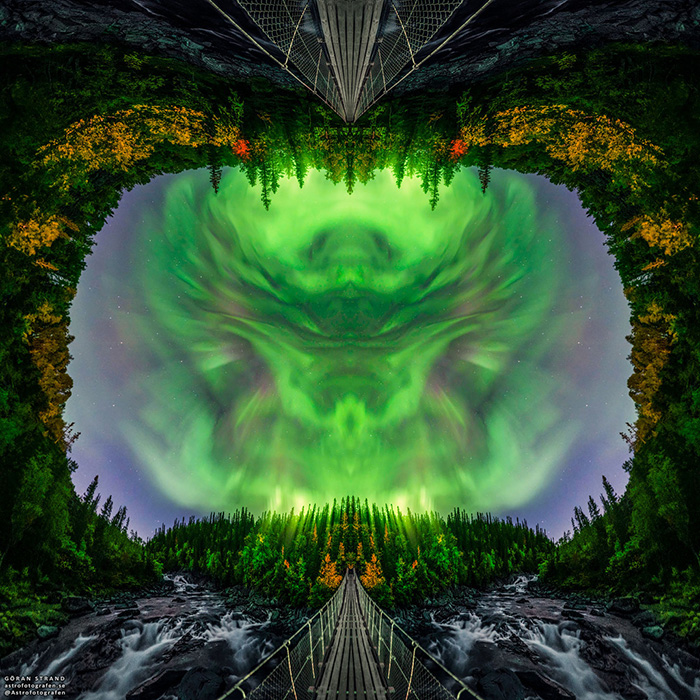

Rorschach Halloween Aurora NASA - October 30, 2021
Explanation: If you see this as a monster's face, don't panic. It's only pareidolia, often experienced as the tendency to see faces in patterns of light and shadow. In fact, the startling visual scene is actually a 180 degree panorama of Northern Lights, digitally mirrored like inkblots on a folded piece of paper. Frames used to construct it were captured on a September night from the middle of a waterfall-crossing suspension bridge in Jamtland, Sweden. With geomagnetic storms triggered by recent solar activity, auroral displays could be very active at planet Earth's high latitudes in the coming days. But if you see a monster's face in your own neighborhood tomorrow night, it might just be Halloween. - Goran Strand
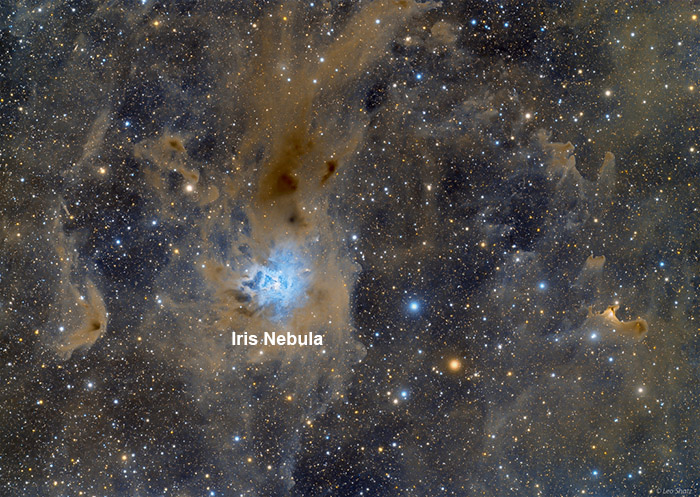

Haunting the Cepheus Flare NASA - October 29, 2021
Explanation: Spooky shapes seem to haunt this dusty expanse, drifting through the night in the royal constellation Cepheus. Of course, the shapes are cosmic dust clouds visible in dimly reflected starlight. Far from your own neighborhood, they lurk above the plane of the Milky Way at the edge of the Cepheus Flare molecular cloud complex some 1,200 light-years away. Over 2 light-years across and brighter than most of the other ghostly apparitions, vdB 141 or Sh2-136 is also known as the Ghost Nebula, seen at the right of the starry field of view. Inside the nebula are the telltale signs of dense cores collapsing in the early stages of star formation. With the eerie hue of dust reflecting bluish light from hot young stars of NGC 7023, the Iris Nebula stands out against the dark just left of center. In the broad telescopic frame, these fertile interstellar dust fields stretch almost seven full moons across the sky. - Leo Shatz
Mirach's Ghost NASA - October 28, 2021
Explanation: As far as ghosts go, Mirach's Ghost isn't really that scary. Mirach's Ghost is just a faint, fuzzy galaxy, well known to astronomers, that happens to be seen nearly along the line-of-sight to Mirach, a bright star. Centered in this star field, Mirach is also called Beta Andromedae. About 200 light-years distant, Mirach is a red giant star, cooler than the Sun but much larger and so intrinsically much brighter than our parent star. In most telescopic views, glare and diffraction spikes tend to hide things that lie near Mirach and make the faint, fuzzy galaxy look like a ghostly internal reflection of the almost overwhelming starlight. Still, appearing in this sharp image just above and to the right of Mirach, Mirach's Ghost is cataloged as galaxy NGC 404 and is estimated to be some 10 million light-years away. - John Chuck
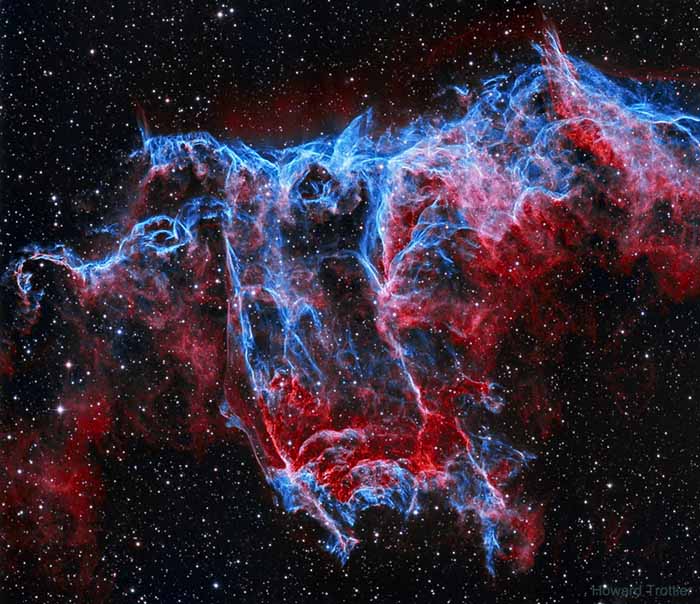
NGC 6995: The Bat Nebula NASA - October 27, 2021
Explanation: Do you see the bat? It haunts this cosmic close-up of the eastern Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, the expanding debris cloud from the death explosion of a massive star. While the Veil is roughly circular in shape and covers nearly 3 degrees on the sky toward the constellation of the Swan (Cygnus), NGC 6995, known informally as the Bat Nebula, spans only 1/2 degree, about the apparent size of the Moon. That translates to 12 light-years at the Veil's estimated distance, a reassuring 1,400 light-years from planet Earth. In the composite of image data recorded through narrow band filters, emission from hydrogen atoms in the remnant is shown in red with strong emission from oxygen atoms shown in hues of blue. Of course, in the western part of the Veil lies another seasonal apparition: the Witch's Broom Nebula. - Howard Trottier
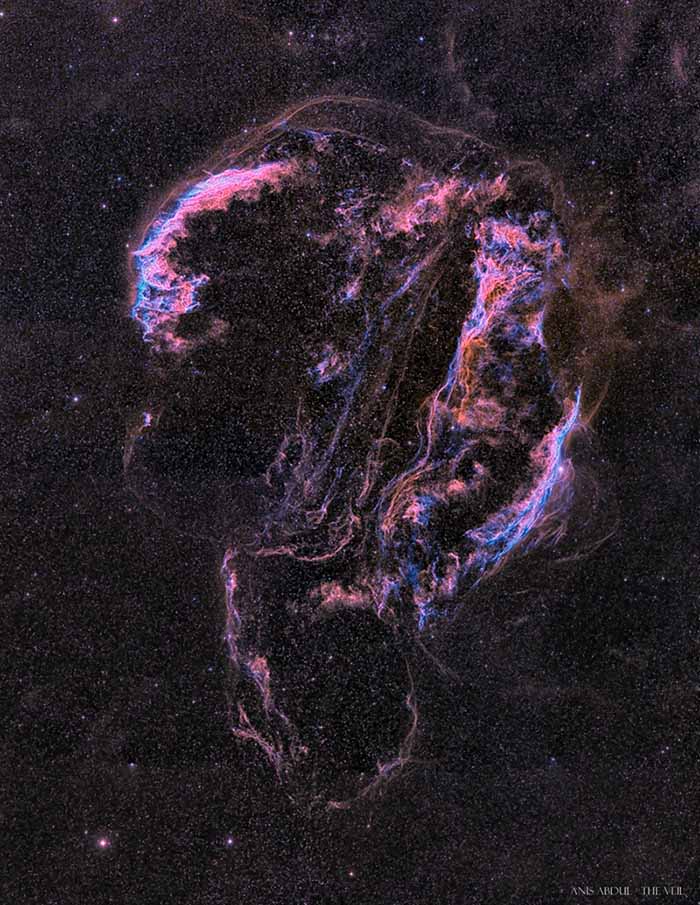
The Ghoul of IC 2118 NASA - October 31, 2020
Explanation: A ghostly visage on a cosmic scale, these remains of shocked, glowing gas haunt planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus and form the Veil Nebula . The nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star. Light from the original supernova explosion likely reached Earth over 5,000 years ago. Also known as the Cygnus Loop, the Veil Nebula now spans nearly 3 degrees or about 6 times the diameter of the full Moon. That translates to over 70 light-years at its estimated distance of 1,500 light-years. In fact, the Veil is so large its brighter parts are recognized as separate nebulae, including The Witch's Broom (NGC 6960) below and right of center. At the top left you can find the Spectre of IC 1340. Happy Halloween! - Anis Abdul

The Ghoul of IC 2118 NASA - October 29, 2020
Explanation: Inspired by the halloween season, this telescopic portrait captures a cosmic cloud with a scary visage. The interstellar scene lies within the dusty expanse of reflection nebula IC 2118 in the constellation Orion, the Hunter. IC 2118 is about 800 light-years from your neighborhood, close to bright bluish star Rigel at Orion's foot. Often identified as the Witch Head nebula for its appearance in a wider field of view it now rises before the witching hour. With spiky stars for eyes, the ghoulish apparition identified here seems to extend an arm many light-years long toward Orion's hot supergiant star. The source of illumination for IC 2118, Rigel is just beyond this frame at the upper left.

It's Halloween! NASA Space Telescope Spots a Ghostly Cosmic Jack-O'Lantern Space.com - October 31, 2019
Outflows of radiation and particles from a massive O-type star carved deep gouges in this nebula, making the cloud of gas and dust look like a spooky jack-o'-lantern. Researchers uncovered the grimacing pumpkin while mapping star formation in the outer region of the Milky Way. A new animation of the nebula outlines the hollowed-out pumpkin, which appears to be screaming into space. The carved-out cloud of gas and dust is caused by the outflow of radiation and particles from a massive O-type star that is 15 to 20 times more massive than the sun

M42: Inside the Orion Nebula NASA - October 30, 2019
The Great Nebula in Orion, an immense, nearby starbirth region, is probably the most famous of all astronomical nebulas. Here, glowing gas surrounds hot young stars at the edge of an immense interstellar molecular cloud only 1500 light-years away. In the featured deep image in assigned colors highlighted by emission in oxygen and hydrogen, wisps and sheets of dust and gas are particularly evident. The Great Nebula in Orion can be found with the unaided eye near the easily identifiable belt of three stars in the popular constellation Orion. In addition to housing a bright open cluster of stars known as the Trapezium, the Orion Nebula contains many stellar nurseries. These nurseries contain much hydrogen gas, hot young stars, proplyds, and stellar jets spewing material at high speeds. Also known as M42, the Orion Nebula spans about 40 light years and is located in the same spiral arm of our Galaxy as the Sun.

NASA shares spooky space photos just in time for Halloween NBC - October 28, 2019
Images shared by NASA this week showcase the spooky wonders of space just ahead of the most unearthly day of the year: Halloween. The agency posted two images to Twitter: one of a celestial phenomenon appearing to be a galactic ghoul, and one of the sun resembling a burning jack-o'-lantern. The "ghostly apparition," as NASA described it Tuesday on Twitter, was actually an image of two galaxies colliding, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in June. "Each 'eye' is the bright core of a galaxy, one of which slammed into another," NASA explained on its website. "The outline of the face is a ring of young blue stars. Other clumps of new stars form a nose and mouth."
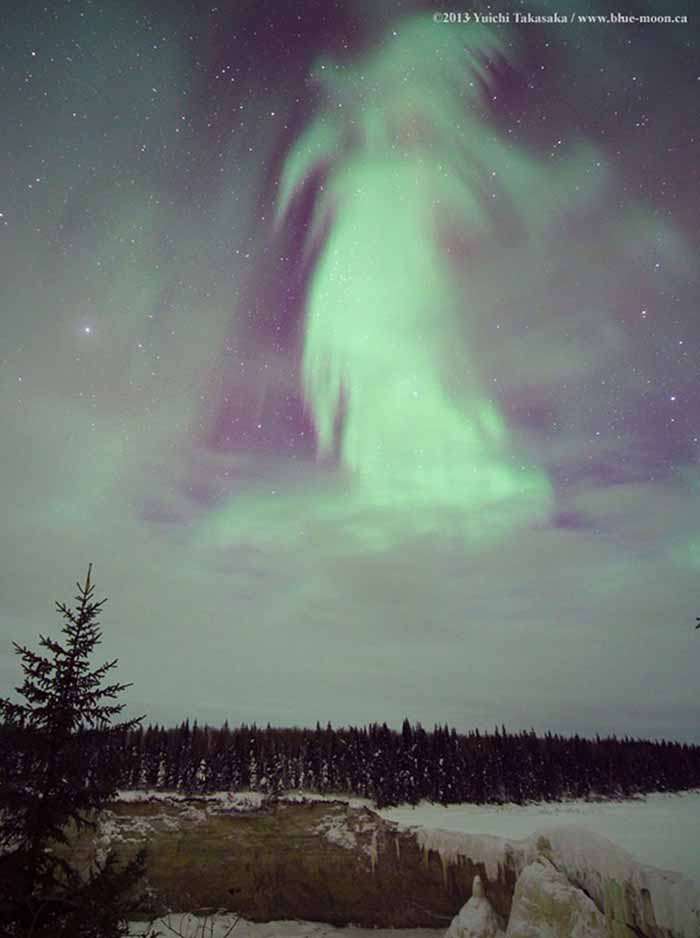

Ghost Aurora over Canada NASA - October 27, 2019
Explanation: What does this aurora look like to you? While braving the cold to watch the skies above northern Canada early one morning in 2013, a most unusual aurora appeared. The aurora definitely appeared to be shaped like something , but what? Two ghostly possibilities recorded by the astrophotographer were "witch" and "goddess of dawn", but please feel free to suggest your own Halloween-enhanced impressions. Regardless of fantastical pareidolic interpretations, the pictured aurora had a typical green color and was surely caused by the scientifically commonplace action of high energy particles from space interacting with oxygen in Earth's upper atmosphere. In the image foreground, at the bottom, is a frozen Alexandra Falls, while evergreen trees cross the middle.- Yuichi Takasaka,
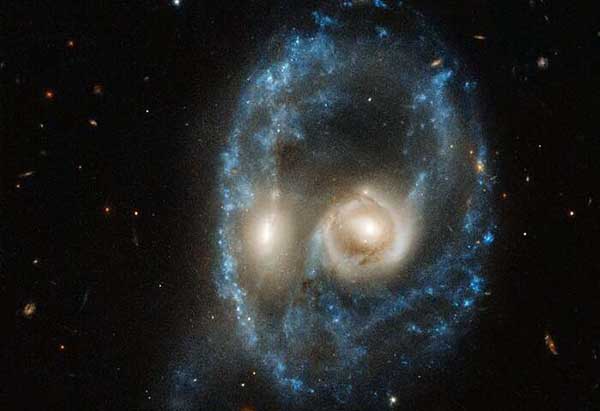

Hubble captures cosmic face Live Science - October 26, 2019
In celebration of Halloween, this new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope captures two galaxies of equal size in a collision that appears to resemble a ghostly face. This observation was made on 19 June 2019 in visible light by the telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys. Although galaxy collisions are common - especially in the early universe - most are not head-on impacts like the collision that likely created this Arp-Madore system 704 million light-years from Earth. This violent encounter gives the system an arresting ring structure, but only for a short amount of time. The crash has pulled and stretched the galaxies' discs of gas, dust, and stars outward, forming the ring of intense star formation that shapes the "nose" and "face" features of the system.
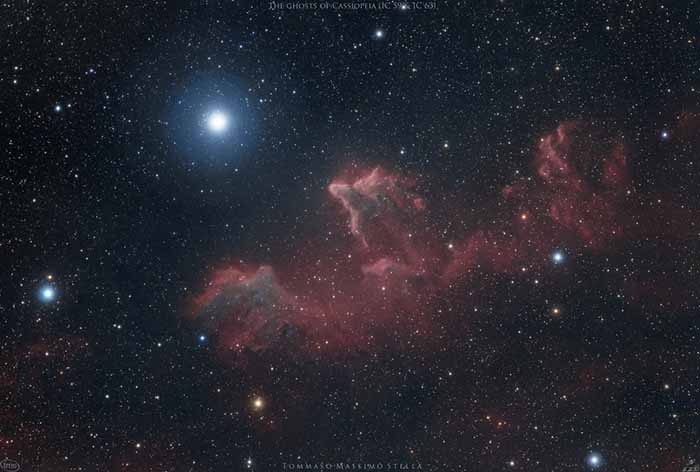

The Ghosts of Cassiopeia NASA - October 25, 2019
Explanation: These bright rims and flowing shapes look ghostly on a cosmic scale. A telescopic view toward the constellation Cassiopeia, the colorful skyscape features swept-back, comet-shaped clouds IC 59 (left) and IC 63. About 600 light-years distant, the clouds aren't actually ghosts. They are slowly disappearing though, under the influence of energetic radiation from hot,luminous star gamma Cas. Gamma Cas is physically located only 3 to 4 light-years from the nebulae, the bright star just above and left in the frame. Slightly closer to gamma Cas, IC 63 is dominated by red H-alpha light emitted as hydrogen atoms ionized by the star's ultraviolet radiation recombine with electrons. Farther from the star, IC 59 shows proportionally less H-alpha emission but more of the characteristic blue tint of dust reflected star light. The field of view spans over 1 degree or 10 light-years at the estimated distance of gamma Cas and friends. - Tommaso Stella
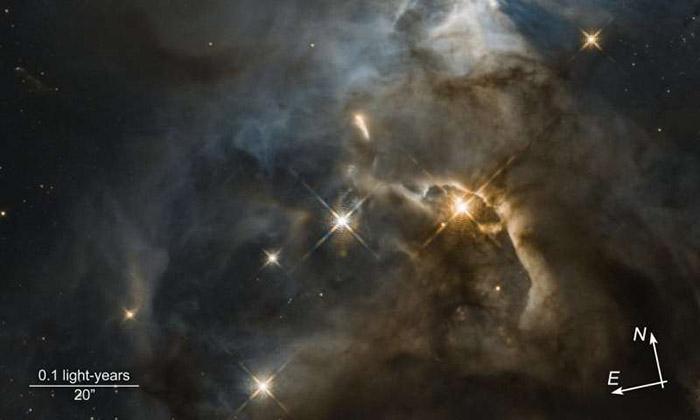

Hubble reveals a giant cosmic 'Bat Shadow'
PhysOrg - October 31, 2018Shadows on Earth can be mysterious and foreboding, but when they occur in space, they can convey information we otherwise could not know. In a stellar nursery called the Serpens Nebula, nearly 1,300 light-years away, a young star's game of shadow play is revealing secrets of its unseen planet-forming disk. The near-infrared vision of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope captured the shadow cast by the fledgling star's brilliant light being blocked by this disk. Named HBC 672, this Sun-like star is surrounded by a debris ring of dust, rock, and iceŅa disk that is too small and too distant to be seen, even by Hubble. But like a little fly that wanders into the beam of a flashlight shining on a wall, its shadow is projected large upon the cloud in which it was born. In this Hubble image, the feature - nicknamed the "Bat Shadow" - spans approximately 200 times the length of our solar system. It is visible in the upper right portion of the picture.
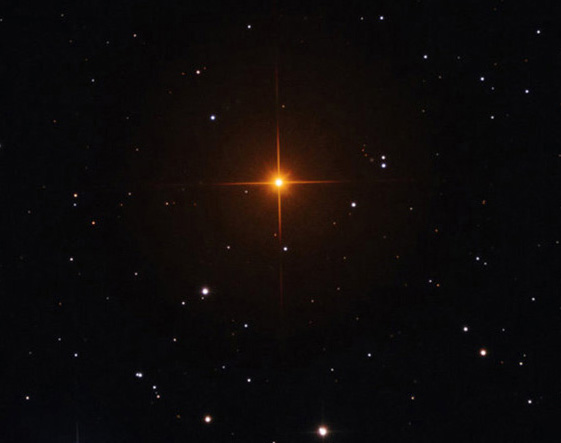

Better known as Hind's Crimson Star, R Leporis is a rare star in planet Earth's night sky. It's also a shocking shade of red. The star's discoverer, 19th century English astronomer John Russell Hind, reported that it appeared in a telescope "... like a drop of blood on a black field." Read More from Astronomy Picture of the Day
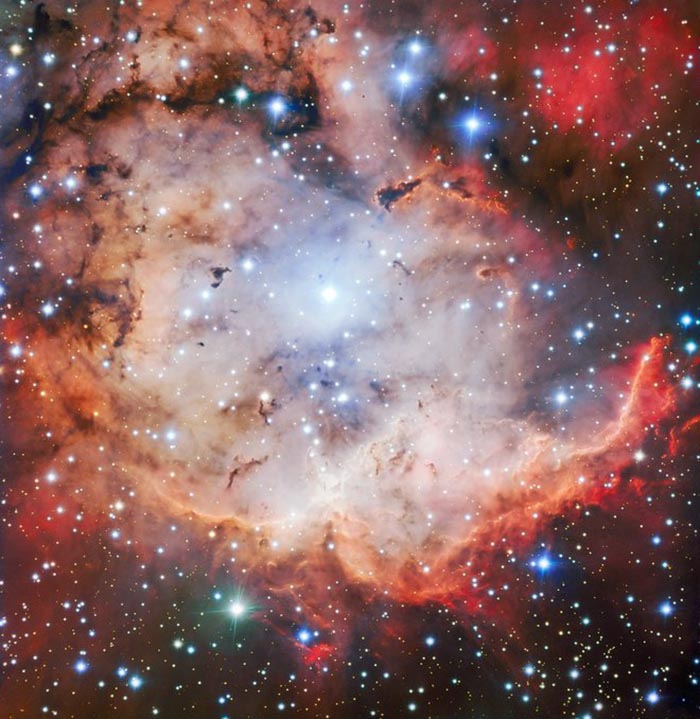

The Skull and Crossbones Nebula
Space.com October 25, 2018To get in the spirit for halloween, the European Southern Observatory has released a new image of the Skull and Crossbones nebula, also known as NGC 2467. Astronomers captured this view using an instrument on the Very Large Telescope array known as the Focal Reducer and low dispersion Spectrograph. - Hanneke Weitering

The Ghost of Cassiopeia
PhysOrg October 25, 2018About 550 light-years away in the constellation of Cassiopeia lies IC 63, a stunning and slightly eerie nebula. Also known as the ghost of Cassiopeia, IC 63 is being shaped by radiation from a nearby unpredictably variable star, Gamma Cassiopeiae, which is slowly eroding away the ghostly cloud of dust and gas. This celestial ghost makes the perfect backdrop for the upcoming feast of All Hallow's Eve - better known as Halloween.
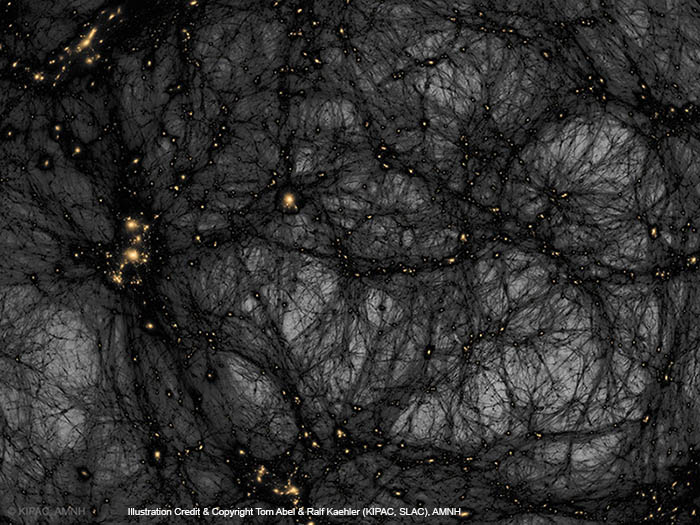
Dark Matter in a Simulated Universe
October 31, 2017Is our universe haunted? It might look that way on this dark matter map. The gravity of unseen dark matter is the leading explanation for why galaxies rotate so fast, why galaxies orbit clusters so fast, why gravitational lenses so strongly deflect light, and why visible matter is distributed as it is both in the local universe and on the cosmic microwave background. The featured image from the American Museum of Natural History's Hayden Planetarium Space Show Dark Universe highlights one example of how pervasive dark matter might haunt our universe. In this frame from a detailed computer simulation, complex filaments of dark matter, shown in black, are strewn about the universe like spider webs, while the relatively rare clumps of familiar baryonic matter are colored orange. These simulations are good statistical matches to astronomical observations. In what is perhaps a scarier turn of events, dark matter -- although quite strange and in an unknown form -- is no longer thought to be the strangest source of gravity in the universe. That honor now falls to dark energy, a more uniform source of repulsive gravity that seems to now dominate the expansion of the entire universe.
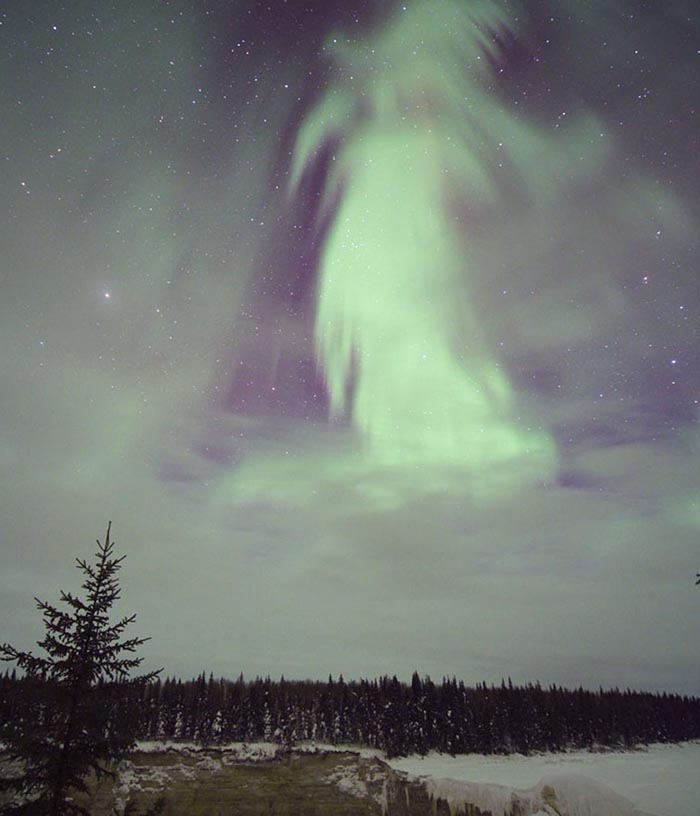

Ghost Aurora over Canada
October 31, 2016What does this aurora look like to you? While braving the cold to watch the skies above northern Canada early one morning in 2013, a most unusual aurora appeared. The aurora definitely appeared to be shaped like something , but what? Two ghostly possibilities recorded by the astrophotographer were "witch" and "goddess of dawn", but please feel free to suggest your own Halloween-enhanced impressions. Regardless of fantastical pareidolic interpretations, the pictured aurora had a typical green color and was surely caused by the scientifically commonplace action of high energy particles from space interacting with oxygen in Earth's upper atmosphere. In the image foreground, at the bottom, is a frozen Alexandra Falls, while evergreen trees cross the middle.
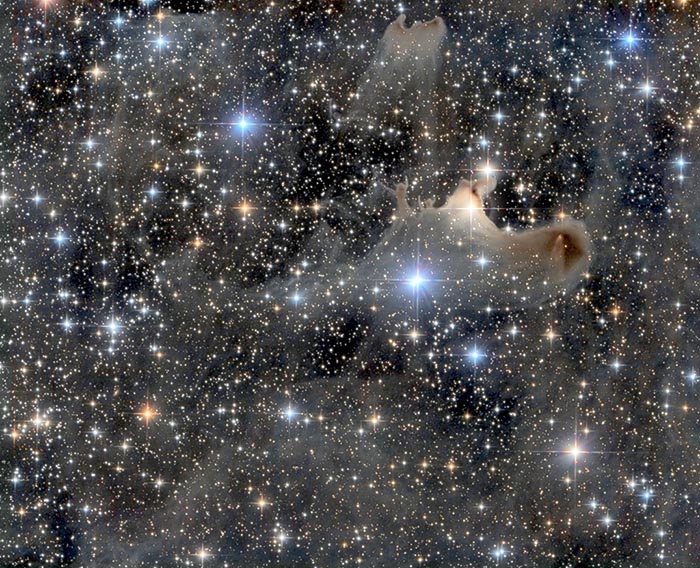

Haunting the Cepheus Flare
October 28, 2016Spooky shapes seem to haunt this jeweled expanse, drifting through the night in the royal constellation Cepheus. Of course, the shapes are cosmic dust clouds faintly visible in dimly reflected starlight. Far from your own neighborhood on planet Earth, they lurk along the plane of the Milky Way at the edge of the Cepheus Flare molecular cloud complex some 1,200 light-years away. Over 2 light-years across and brighter than the other ghostly apparitions, vdB 141 or Sh2-136 is also known as the Ghost Nebula, seen at the right of the starry field of view. Within the nebula are the telltale signs of dense cores collapsing in the early stages of star formation.
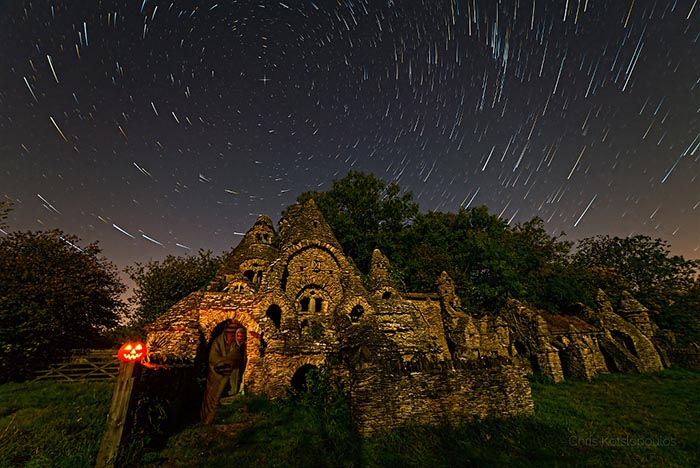

Ghosts and Star Trails
October 31, 2015Don't be scared. Stars won't fall from the sky and ghosts won't really haunt your neighborhood tonight. But it looks like they might be doing just that in this eerie picture of an eccentric old abandoned house in moonlight. A treat for the eye the image is a trick of stacked multiple exposures, 60 frames exposed for 25 seconds each. While the digital frames were recorded with a camera fixed to a tripod stars traced concentric arcs about the north celestial pole, only a reflection of planet Earth's rotation on its axis. Conveniently marked by bright star Polaris, the pole could be positioned above the peaks of the deserted dwelling. Wrapped in a blanket to stay warm, the photographer's own movements during the exposures were blended into the ghostly apparitions. Of course, the grinning Jack-o-Lantern is there to wish you a safe and Happy Halloween!
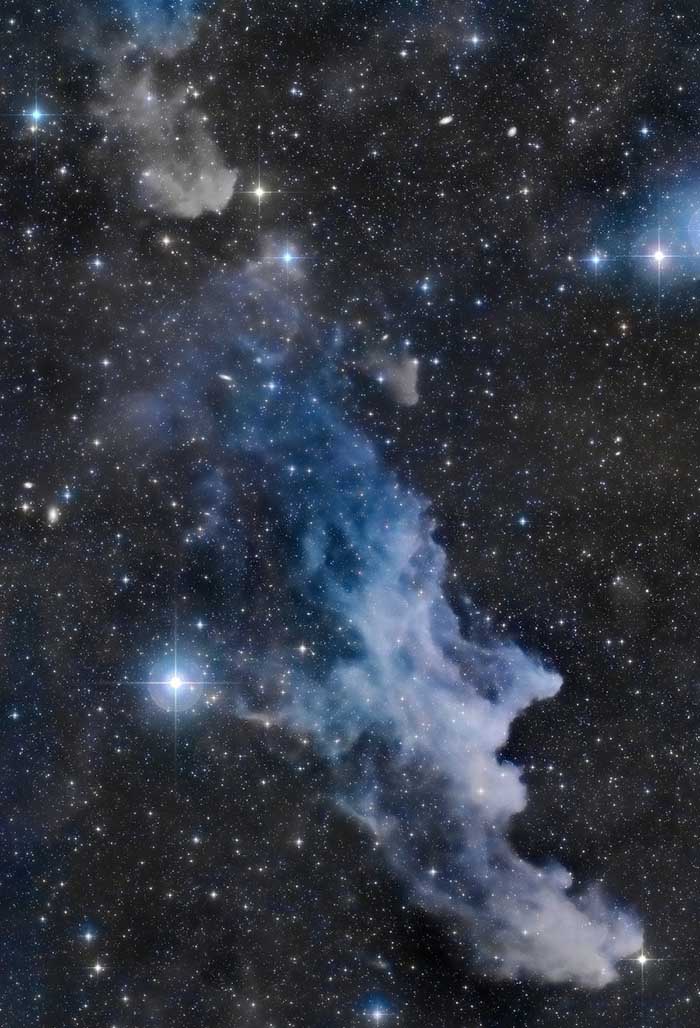

The Witch Head Nebula
October 30, 2015Double, double toil and trouble; Fire burn, and cauldron bubble .... maybe Macbeth should have consulted the Witch Head Nebula. A suggestively shaped reflection nebula, this cosmic crone is about 800 light-years away though. Its frightening visage seems to glare toward nearby bright star Rigel in Orion, just off the right edge of this frame. More formally known as IC 2118, the interstellar cloud of dust and gas is nearly 70 light-years across, its dust grains reflecting Rigel's starlight. In this composite portrait, the nebula's color is caused not only by the star's intense bluish light but because the dust grains scatter blue light more efficiently than red. The same physical process causes Earth's daytime sky to appear blue, although the scatterers in planet Earth's atmosphere are molecules of nitrogen and oxygen.
The Day After Mars
November 1, 2014Explanation: October 31, 1938 was the day after Martians encountered planet Earth, and everything was calm. Reports of the invasion were revealed to be part of a Halloween radio drama, the now famous broadcast based on H.G. Wells' scifi novel War of the Worlds. On Mars October 20, 2014 was calm too, the day after its close encounter with Comet Siding Spring. Not a hoax, this comet really did come within 86,700 miles or so of Mars, about 1/3 the Earth-Moon distance. Earth's spacecraft and rovers in Mars orbit and on the surface reported no ill effects though, and had a ringside seat as a visitor from the outer solar system passed by. Spanning over 2 degrees against stars of the constellation Ophiuchus, this colorful telescopic snapshot captures our view of Mars on the day after. Bluish star 51 Ophiuchi is at the upper right and the comet is just emerging from the Red Planet's bright glare.
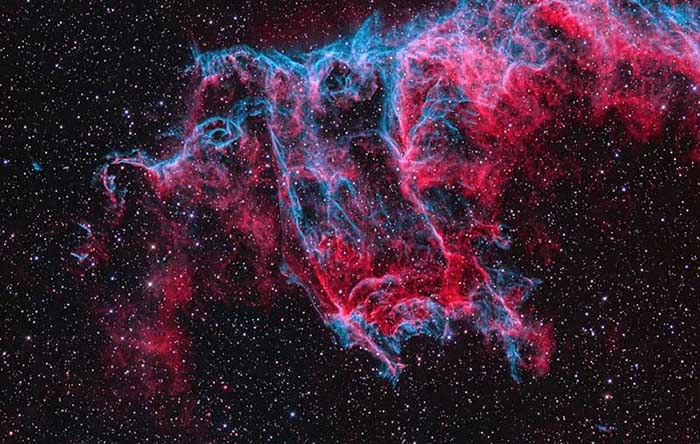

A Spectre in the Eastern Veil
October 30, 2014Explanation: Frightening forms and scary faces are a mark of the Halloween season. They also haunt this cosmic close-up of the eastern Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, the expanding debris cloud from the death explosion of a massive star. While the Veil is roughly circular in shape and covers nearly 3 degrees on the sky in the constellation Cygnus, this portion of the eastern Veil spans only 1/2 degree, about the apparent size of the Moon. That translates to 12 light-years at the Veil's estimated distance, a reassuring 1,400 light-years from planet Earth. In the composite of image data recorded through broad and narrow band filters, emission from hydrogen atoms in the remnant is shown in red with strong emission from oxygen atoms in blue-green hues. Of course, in the western part of the Veil lies another seasonal apparition, the Witch's Broom.

Night on a Spooky Planet
October 31, 2013Explanation: What spooky planet is this? Planet Earth of course, on the dark and stormy night of September 12 at Hverir, a geothermally active area along the volcanic landscape in northeastern Iceland. Geomagnetic storms produced the auroral display in the starry night sky while ghostly towers of steam and gas venting from fumaroles danced against the eerie greenish light. Tonight, there is still a chance for geomagnetic storms triggered by recent solar activity, so high-latitude skygazers should beware. And ghostly shapes may dance in your neighborhood, too. Have a safe and Happy Halloween!
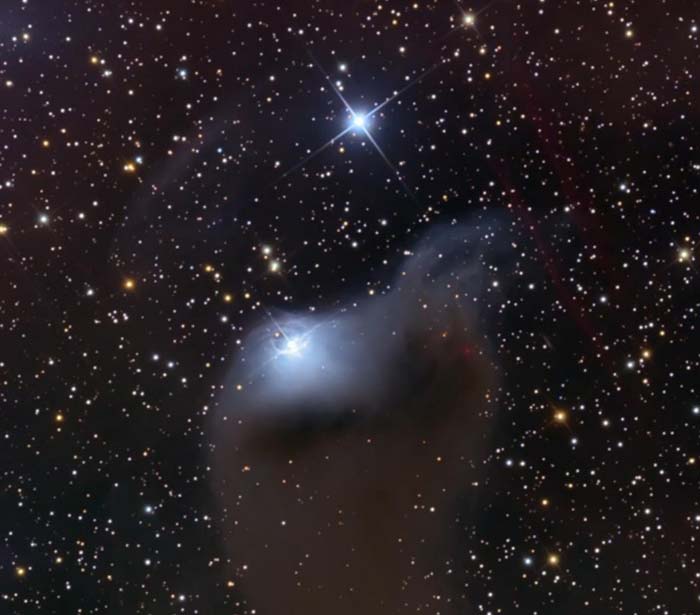

VdB 152: A Ghost in Cepheus
October 31, 2012Explanation: Described as a "dusty curtain" or "ghostly apparition", mysterious reflection nebula VdB 152 really is very faint. Far from your neighborhood on this Halloween Night, the cosmic phantom is nearly 1,400 light-years away. Also catalogued as Ced 201, it lies along the northern Milky Way in the royal constellation Cepheus. Near the edge of a large molecular cloud, pockets of interstellar dust in the region block light from background stars or scatter light from the embedded bright star giving parts of the nebula a characteristic blue color. Ultraviolet light from the star is also thought to cause a dim reddish luminescence in the nebular dust. Though stars do form in molecular clouds, this star seems to have only accidentally wandered into the area, as its measured velocity through space is very different from the cloud's velocity. This deep telescopic image of the region spans about 7 light-years.
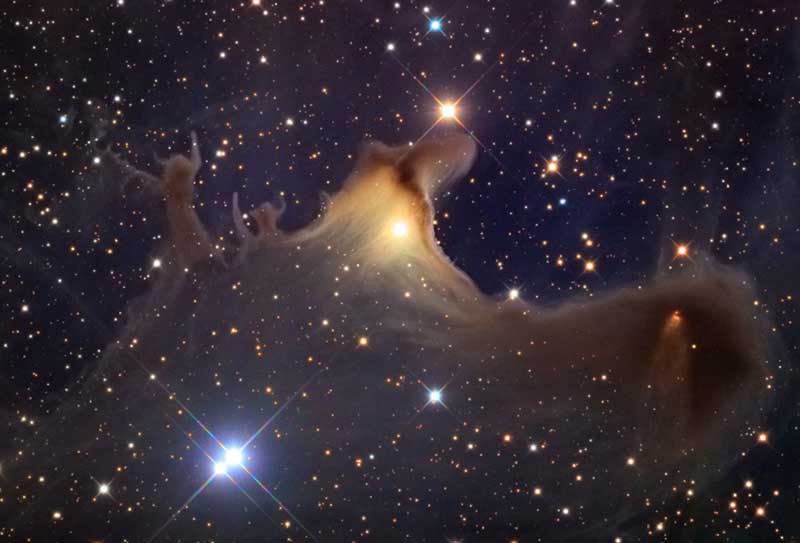

Ghost of the Cepheus Flare
October 31, 2011Explanation: Spooky shapes seem to haunt this starry expanse, drifting through the night in the royal constellation Cepheus. Of course, the shapes are cosmic dust clouds faintly visible in dimly reflected starlight. Far from your own neighborhood on planet Earth, they lurk at the edge of the Cepheus Flare molecular cloud complex some 1,200 light-years away. Over 2 light-years across the ghostly nebula and relatively isolated Bok globule, also known as vdB 141 or Sh2-136, is near the center of the field. The core of the dark cloud on the right is collapsing and is likely a binary star system in the early stages of formation. Even so, if the spooky shapes could talk, they might well wish you a happy Halloween.
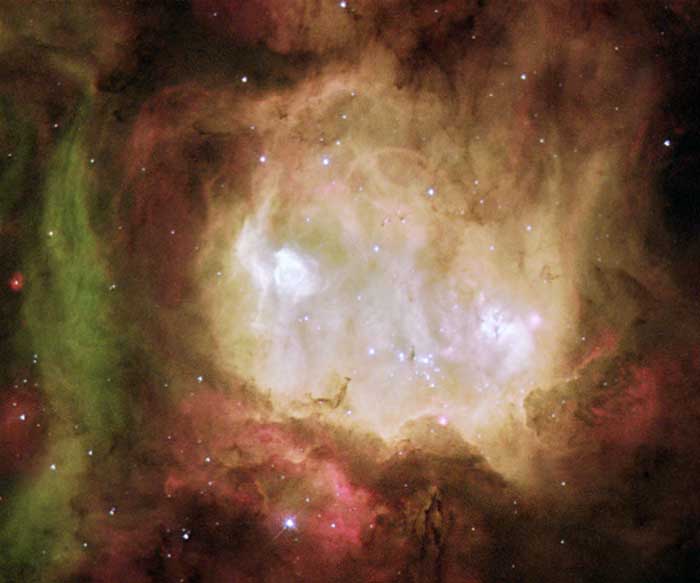

Halloween and the Ghost Head Nebula
October 31, 2010Explanation: Halloween's origin is ancient and astronomical. Since the fifth century BC, Halloween has been celebrated as a cross-quarter day, a day halfway between an equinox (equal day / equal night) and a solstice (minimum day / maximum night in the northern hemisphere). With a modern calendar, however, the real cross-quarter day will occur next week. Another cross-quarter day is Groundhog's Day. Halloween's modern celebration retains historic roots in dressing to scare away the spirits of the dead. Perhaps a fitting tribute to this ancient holiday is this view of the Ghost Head Nebula taken with the Hubble Space Telescope. Similar to the icon of a fictional ghost, NGC 2080 is actually a star forming region in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of our own Milky Way Galaxy. The Ghost Head Nebula spans about 50 light-years and is shown in representative colors.

Star Trails and the Captain's Ghost
October 29, 2010Explanation: Look closely at this surreal nightscape. In the dreamlike scene, star trails arc over an old ship run aground on a beach near Gytheio, Peloponnesus in southern Greece. Could that be the captain's ghost haunting the beach, gazing forlornly at the decaying wreck, hovering over starlight reflected in still water? Actually, the ephemeral shape is the photographer. Instead of a single long exposure to record the motion of the stars as the Earth rotates on its axis, the picture is composed of 90 consecutive images, each exposure 90 seconds long. Digitally stacking the individual exposures then reconstructs the star trails. It also creates a ghostly, semi-transparent figure of the photographer who was captured standing on the beach in only one of the exposures.
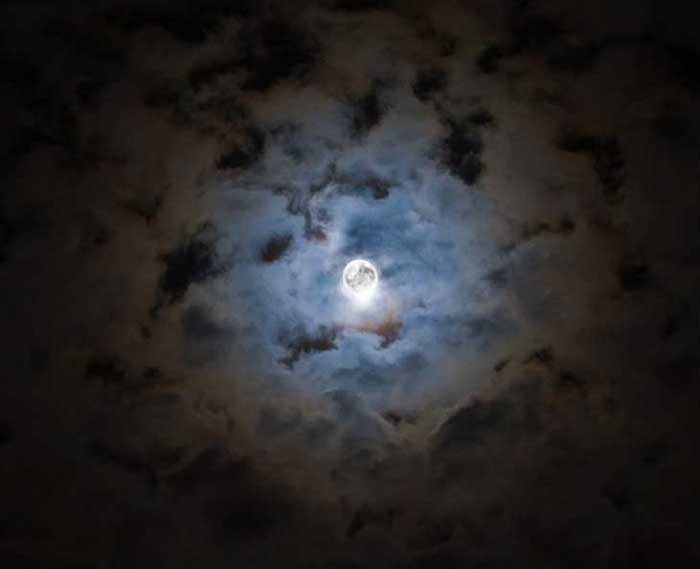

Halloween's Moon
November 5, 2009Explanation: Illuminating the landscape all through the night of November 2nd, this week's bright Full Moon was known in the northern hemisphere as a Hunter's Moon. But this dramatic view of the shining lunar orb, from Sobreda, Portugal, was captured just a few nights earlier, on Halloween. In the spirit of the season, the image plays a little trick. The picture is actually two digital photos - one short and one long exposure. They were combined to bring out the details of the bright lunar surface and the fainter features in the dark, surrounding clouds, in a single image. Of course, you may recognize some of the spookier shapes in the clouds as having visited your neighborhood last week, along with Halloween's Moon.
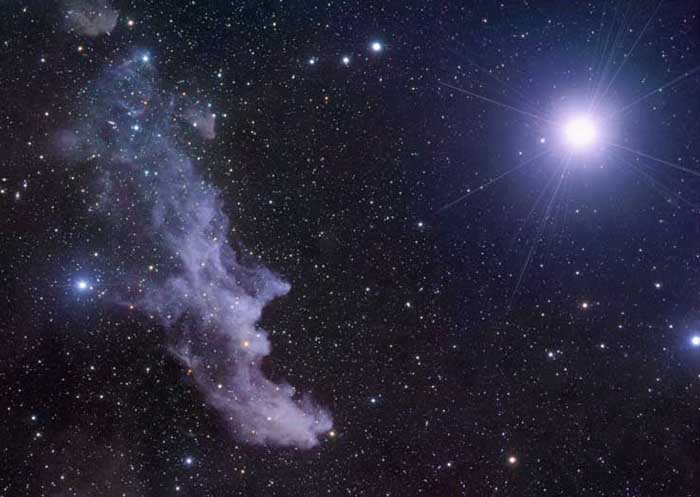

A Witch by Starlight
October 31, 2008Explanation: By starlight this eerie visage shines in the dark, a crooked profile evoking its popular name, the Witch Head Nebula. In fact, this entrancing telescopic portrait gives the impression the witch has fixed her gaze on Orion's bright supergiant star Rigel. Spanning over 50 light-years, the dusty cosmic cloud strongly reflects nearby Rigel's blue light, giving it the characteristic color of a reflection nebula. Cataloged as IC 2118, the Witch Head Nebula is about 1,000 light-years away. Of course, you might see a witch this scary tonight, but don't panic. Have a safe and Happy Halloween!
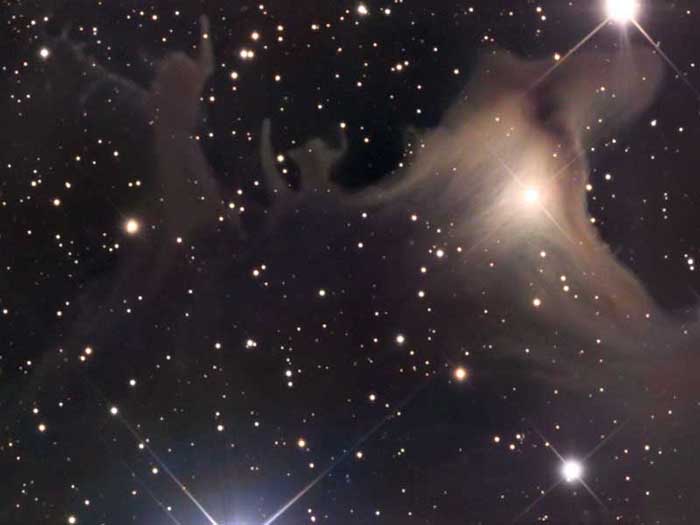

SH2 136: A Spooky Nebula
October 31, 2006Explanation: The dark nebula SH2-136 appears to be celebrating Halloween all of the time. The complex process of star formation create dust clouds of many shapes and sizes -- it is human perception that might identify a ghoulish creature, on the right of the above image, chasing humans. Halloween's modern celebration retains historic roots in dressing to scare away the spirits of the dead. Since the fifth century BC, Halloween has been celebrated as a cross-quarter day, a day halfway between an equinox (equal day / equal night) and a solstice (minimum day / maximum night in the northern hemisphere). With our modern calendar, however, the real cross-quarter day will occur next week. Other cross-quarter markers include Groundhog Day and Walpurgis Night.
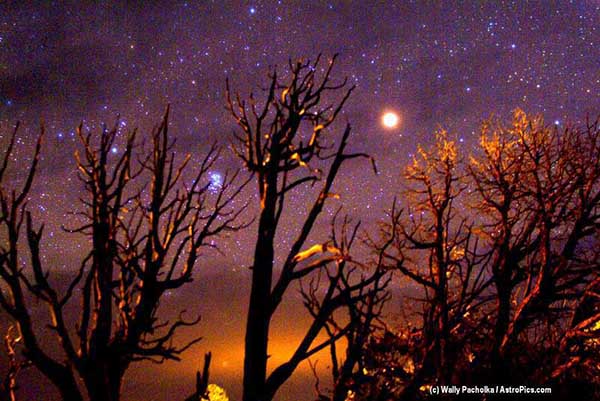

Martian Halloween
October 31, 2005Explanation: From sunset to sunrise, an unusually bright yellowish orb will hang in the sky this Halloween: Mars. Yesterday, Earth passed Mars as they orbited the Sun, bringing Mars closer than it will be for the next thirteen years. Tonight though, Mars will be nearly as bright as last night, a beacon of extraterrestrial spookiness. Opposite the Sun, Mars will rise just when the Sun sets, set just when the Sun rises, and be visible the entire night. Mars will not always be the brightest object in tonight's sky, though. Brighter than even Mars, almost spooky Venus will light up the western horizon for a brief time just after sunset. Please have a safe and happy All Hallows Eve.
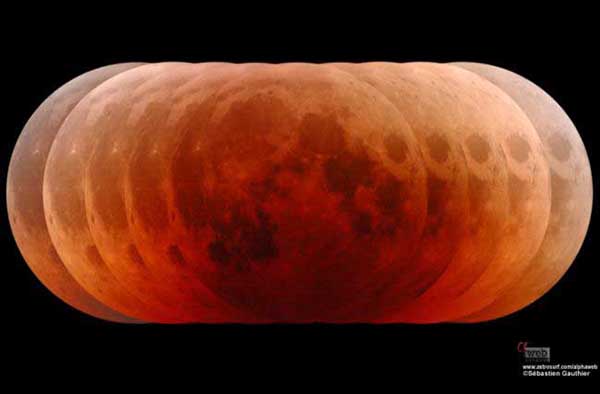
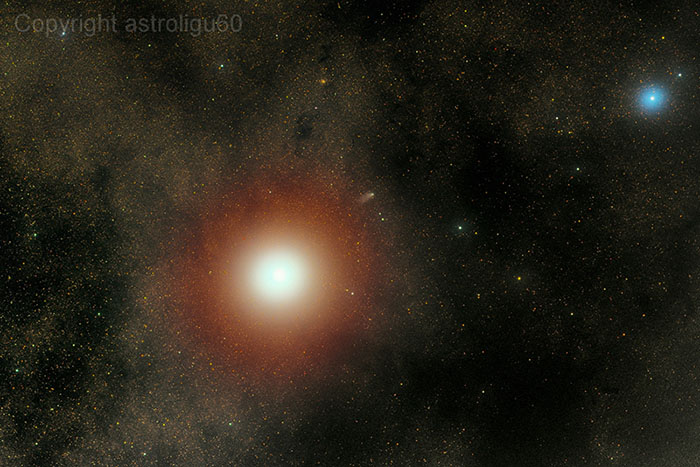
Pumpkin Moon
October 31, 2004Explanation: Does this look familiar? Red and orange hues haunting the face of the Moon should remind you of the October 27th total lunar eclipse. Created from exposures taken at intervals of 8.5 minutes during the total eclipse phase, the midpoint of the eclipse corresponds to the central exposure. The play of light across the lunar surface nicely demonstrates that the Earth's shadow is not uniformly dark as it extends into space. In fact, lunar maria and montes are still visible in the dimmed, reddened sunlight scattered into the cone-shaped shadow region, or umbra, by the atmosphere. Still, while processing the pictures into this composite image, astronomer Sebastien Gauthier was reminded of another haunting orange face. Have a safe and happy Halloween!
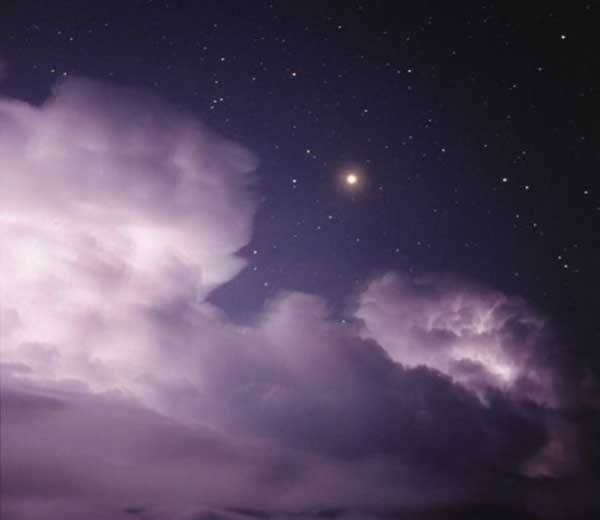

A Dark and Stormy Night
October 31, 2003Explanation: It was a dark and stormy night. But on August 29th the red planet Mars, near its closest approach to Earth in almost 60,000 years, shone brightly in the sky against a background of stars in the constellation Aquarius. In the foreground of this scary view, huge thunder clouds are lit by lightning strokes from within. Mars, of course, has nothing to do with storms on Earth, though both have the power to excite the imagination and wonder of Earthdwellers. And who knows what luminous sights you might see if you go out tonight? Have a safe and Happy Halloween!

Aurora Halloween
October 31, 2002Explanation: For much of the month of October, traveling shock waves from the Sun and solar wind gusts have buffeted planet Earth's magnetosphere. As a result, skywatchers at high latitudes in the northern hemisphere were treated to many displays of the aurora borealis or northern lights. For example, on the first of October this particularly ghostly apparition was photographed looming above the horizon near the town of Inari in northern Finnish Lapland. But the solar wind is dying down for now. So if you just happen to be out tonight and you see such a specter haunting your skies ... it may not be an aurora. Have a safe and happy Halloween!
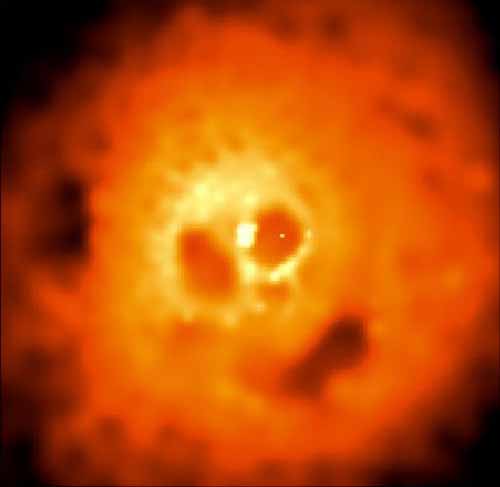
Perseus Cluster's X-Ray Skull
October 31, 2000Explanation: This haunting image from the orbiting Chandra Observatory reveals the Perseus Cluster of Galaxies in x-rays, photons with a thousand or more times the energy of visible light. Three hundred twenty million light-years distant, the Perseus Cluster contains thousands of galaxies, but none of them are seen here. Instead of mere galaxies, a fifty million degree cloud of intracluster gas, itself more massive than all the cluster's galaxies combined, dominates the x-ray view. From this angle, voids and bright knots in the x-ray hot gas cloud lend it a very suggestive appearance. Like eyes in a skull, two dark bubbles flank a bright central source of x-ray emission. A third elongated bubble (at about 5 o'clock) forms a toothless mouth. The bright x-ray source is likely a supermassive black hole at the cluster center with the bubbles blown by explosions of energetic particles ejected from the black hole and expanding into the immense gas cloud. Fittingly, the dark spot forming the skull's "nose" is an x-ray shadow ... the shadow of a large galaxy inexorably falling into the cluster center. Over a hundred thousand light-years across, the Perseus Cluster's x-ray skull is a bit larger than skulls you may see tonight. Have a safe and happy Halloween!

The Cat's Eye Nebula
October 31, 1999Explanation: Three thousand light-years away, a dying star throws off shells of glowing gas. This image from the Hubble Space Telescope reveals The Cat's Eye Nebula to be one of the most complex planetary nebulae known. In fact, the features seen in the Cat's Eye are so complex that astronomers suspect the bright central object may actually be a binary star system. The term planetary nebula, used to describe this general class of objects, is misleading. Although these objects may appear round and planet-like in small telescopes, high resolution images reveal them to be stars surrounded by cocoons of gas blown off in the late stages of stellar evolution. On planet Earth, of course, cats and other creatures may be on the prowl tonight. Keep your eyes peeled and have a safe and happy Halloween!

Bats And The Barren Moon
October 31, 1998Explanation: This picture, taken as the Apollo 17 astronauts orbited the Moon in 1972, depicts the stark lunar surface around the Eratosthenes and Copernicus craters. Images of a Moon devoid of life are familiar to denizens of the space age. Contrary to this modern perception, life on the Moon was reported in August of 1835 in a series of sensational stories first published by the New York Sun - apparently intended to improve the paper's circulation. These descriptions of lunar life received broad credence and became one of the most spectacular hoaxes in history. Supposedly based on telescopic observations, the stories featured full, lavish accounts of a Moon with oceans and beaches, teeming with plant and animal life and climaxing with reported sightings of winged, furry, human-like creatures resembling bats ! Within a month the trick had been revealed but the newspaper continued to enjoy an increased readership. For now ... have a safe and happy Halloween !
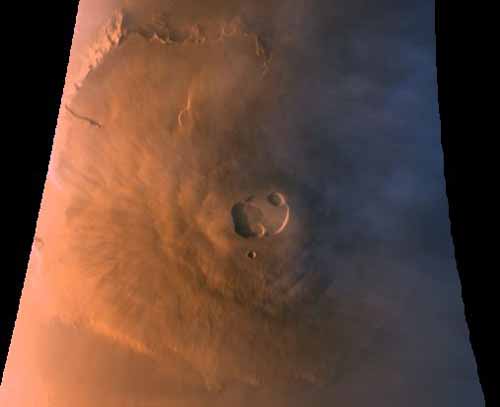

Haunting Mars
October 31, 1997Explanation: This Halloween, the news about Mars is good news - Mars Global Surveyor will resume aerobraking into a mapping orbit around the haunting red planet. Wide angle cameras onboard the spacecraft recently recorded this shadowy image of Olympus Mons, the Solar System's largest volcano, from an altitude of over 100 miles. The summit depression or caldera of Olympus Mons is about 40 miles across and 15 miles above the Martian surface. On Halloween Night in 1938, Mars also made the news when Orson Welles' radio theatre adaptation of H.G. Wells' "War of the Worlds" - a fictional account of invaders from Mars - was dramatized as a live news report. The performance was so convincing it tricked some listeners, but most who heard the broadcast felt it was a treat. Have a happy and safe Halloween!
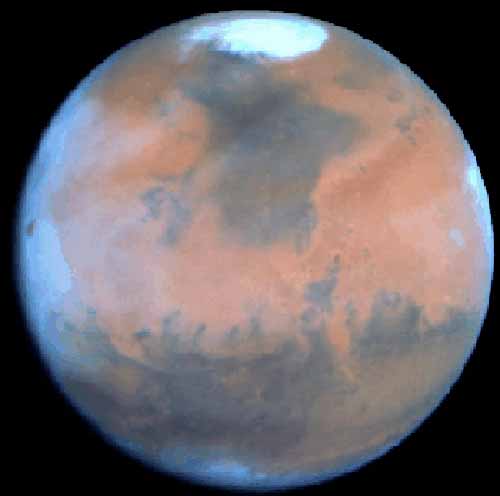

A Halloween Invasion from Mars
NASA - October 31, 1995Explanation: Orson Welles became an instant legend on Halloween in 1938 for his radio dramatization of H.G. Wells' "War of the Worlds". Some listeners who did not realize it was a theatrical production were driven to near panic by this fictional account of invaders from Mars. In the story, as in the above Hubble Space Telescope image, Mars was at "opposition", its point of closest approach to the Earth, a distance of some 65 million miles. For the Martians, it was imagined that this was a good time to invade. For astronomers, opposition is a good time to study the red planet and this HST image, represents the clearest view of Mars ever for an Earth telescope. The icy north polar cap is visible at the top of the picture as well as a veil of white clouds along the planet's left edge. The dark markings represent areas where the reddish tinged dust characteristic of the surface has been blown away by the Martian winds.