
Bears are mammals of the family Ursidae. Bears are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans, with the pinnipeds being their closest living relatives. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Northern Hemisphere and partially in the Southern Hemisphere. Bears are found on the continents of North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
Common characteristics of modern bears include large bodies with stocky legs, long snouts, shaggy hair, plantigrade paws with five nonretractile claws, and short tails. While the polar bear is mostly carnivorous, and the giant panda feeds almost entirely on bamboo, the remaining six species are omnivorous with varied diets.
With the exception of courting individuals and mothers with their young, bears are typically solitary animals. They are generally diurnal, but may be active during the night (nocturnal) or twilight (crepuscular), particularly around humans. Bears possess an excellent sense of smell and, despite their heavy build and awkward gait, are adept runners, climbers, and swimmers. In autumn, some bear species forage large amounts of fermented fruits, which affects their behavior. Bears use shelters, such as caves and burrows, as their dens; most species occupy their dens during the winter for a long period (up to 100 days) of sleep similar to hibernation.
Bears have been hunted since prehistoric times for their meat and fur. With their tremendous physical presence and charisma, they play a prominent role in the Arts, mythology, and other cultural aspects of various human societies. In modern times, the bears' existence has been pressured through the encroachment on their habitats and the illegal trade of bears and bear parts, including the Asian bile bear market. The IUCN lists six bear species as vulnerable or endangered, and even least concern species, such as the brown bear, are at risk of extirpation in certain countries. The poaching and international trade of these most threatened populations are prohibited, but still ongoing. Continue reading
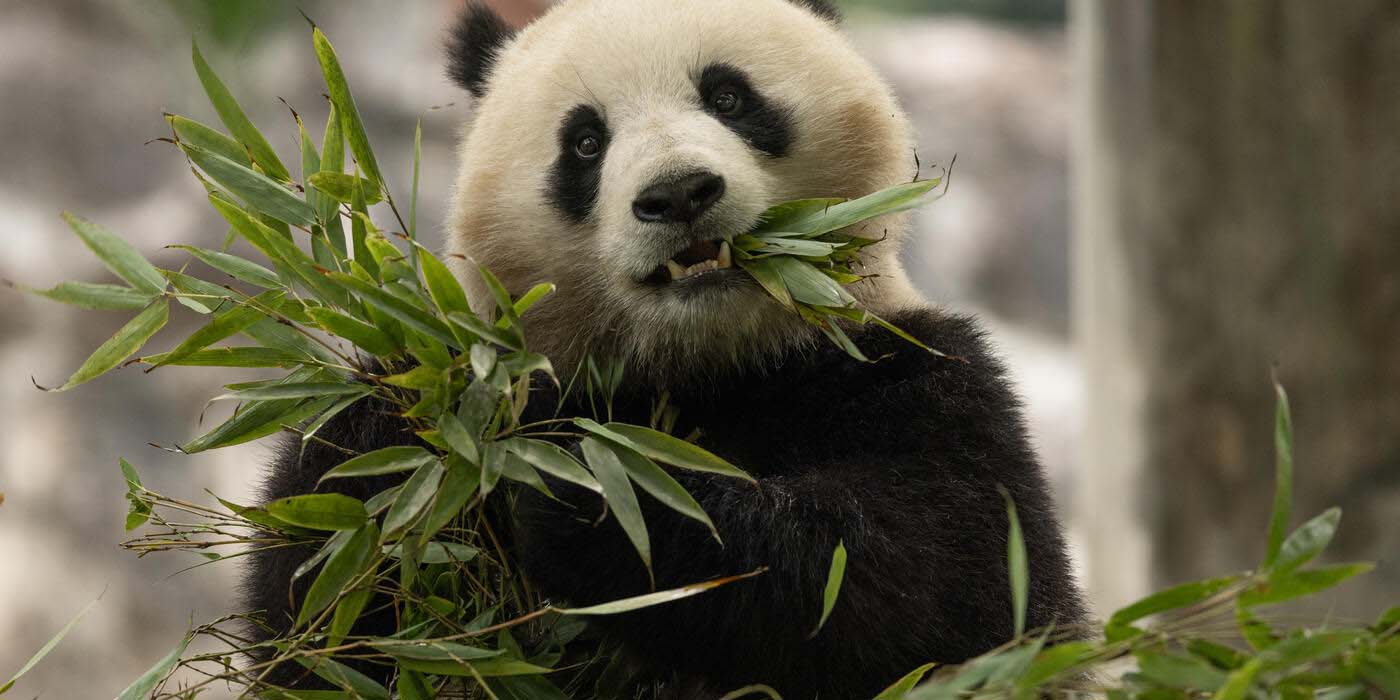

The giant panda is native to south central China. It is easily recognized by the large, distinctive black patches around its eyes, over the ears, and across its round body. The name "giant panda" is sometimes used to distinguish it from the unrelated red panda. Though it belongs to the order Carnivora, the giant panda's diet is over 99% bamboo. Giant pandas in the wild will occasionally eat other grasses, wild tubers, or even meat in the form of birds, rodents or carrion. In captivity, they may receive honey, eggs, fish, yams, shrub leaves, oranges, or bananas along with specially prepared food. Read more ..
CNN: 25 baby pandas make first public appearance CNN- January 23, 2023
Ahead of the Lunar New Year next week, two Chinese panda research centers collaborated to debut their 25 newborn pandas to promote projects including protection, international exchanges and scientific research.
Giant pandas Bao Li and Qing Bao make public debut at National Zoo ABC - January 24, 2025
First photos of new pandas Yun Chuan and Xin Bao in their new habitat at San Diego Zoo ABC - July 10, 2024
Mystery Of World's Only Captive Brown And White Panda Solved With Genetics IFL Science - March 5, 2024
Unique Albino Panda Spotted in China, Sans Eye Mask Science Alert - June 2, 2023
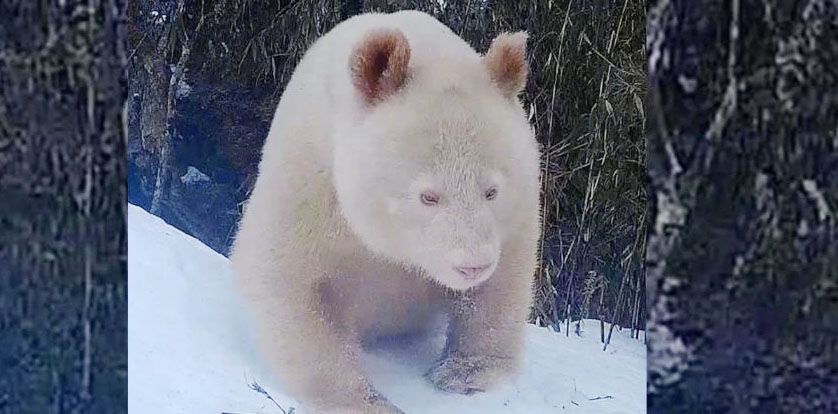

Why pandas are black and white Science Daily - March 3, 2017

Scientists who answered why zebras have black and white stripes pose the question to pandas. The giant panda's distinct black-and-white markings have two functions: camouflage and communication. The study found that most of the panda - its face, neck, belly, rump - is white to help it hide in snowy habitats. The arms and legs are black, helping it to hide in shade.
Video of bear at a Chinese zoo has people asking: Is that a bear or human in costume?
Today Show - August 2, 2023
The intrigue began when footage of Angela, a Malayan sun bear, standing on her hind legs at Hangzhou Zoo in the eastern province of Zhejiang spread on Douyin, a TikTok-style social media site, last month.

A grizzly-polar-bear-hybrid (also named grolar bear, pizzly bear, zebra bear, grizzlar, or nanulak) is a rare ursid hybrid that has occurred both in captivity and in the wild. In 2006, the occurrence of this hybrid in nature was confirmed by testing the DNA of a unique-looking bear who had been shot near Sachs Harbour, Northwest Territories, on Banks Island in the Canadian Arctic. The number of confirmed hybrids has since risen to eight, all of them descending from the same female polar bear.
Possible wild-bred polar-grizzly-hybrids have been reported and shot in the past, but DNA-tests were not available to verify the bears' ancestry.
Genetic analysis has revealed multiple instances of introgressive hybridization between bear species, including introgression of polar bear DNA into brown bears during the Pleistocene ("grizzly bear" is a local common name for Ursus arctos whereas "brown bear" is used internationally and in science to refer to the species as a whole). Continue reading
Grolar Bear Hybrids (Grizzly-Polar) Are Extremely Rare, With Just 8 Confirmed IFL Science - June 14, 2024
Grizzly bears in the Arctic are becoming an increasingly common occurrence as the planet warms, which means that they are beginning to encroach on polar bear territory more regularly. As a result, scientists have found evidence of polar-grizzly hybrids, but new research has confirmed that these grolar bears remain extremely rare. Polar bear and grizzly bear hybrids come in two forms: grolar bears and pizzlies, and the difference comes down to the offspring's parentage. A grolar bear is the offspring of a grizzly bear male and polar bear female, while a pizzly bear is the offspring of a polar bear male and grizzly female.
All wild hybrids between polar bears and grizzlies - that is, all the hybrids we know of that exist outside of zoo care - are grolar bears, defined by having a grizzly father and a mother who is either a polar bear or a hybrid. As for why that is, it largely comes down to logistics.
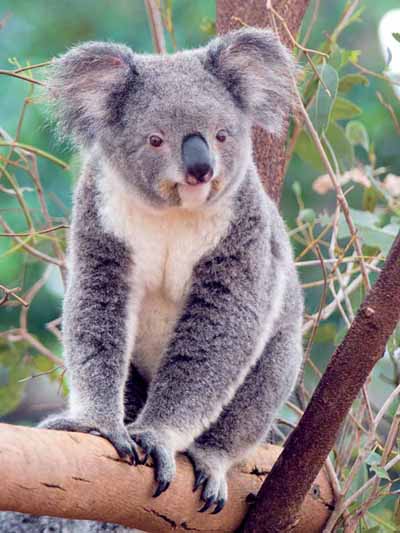

The koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia, and the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae.
The koala is found in coastal regions of eastern and southern Australia, from near Adelaide to the southern part of Cape York Peninsula. Populations also extend for considerable distances inland in regions with enough moisture to support suitable woodlands. The koalas of South Australia were largely exterminated during the early part of the 20th century, but the state has since been repopulated with Victorian stock. The koala is not found in Tasmania or Western Australia. Continue reading
Motherhood
Resurrection
Bravery
Peace
Power
Benevolence
Sovereignty
Duality
Yin
Feminine
Moon
Winter
Inaction
Darkness
Introspection
Subconscious
Yang
Masculine
Sun
Action
Spring/Summer
Lightness
Extroversion
Consciousness
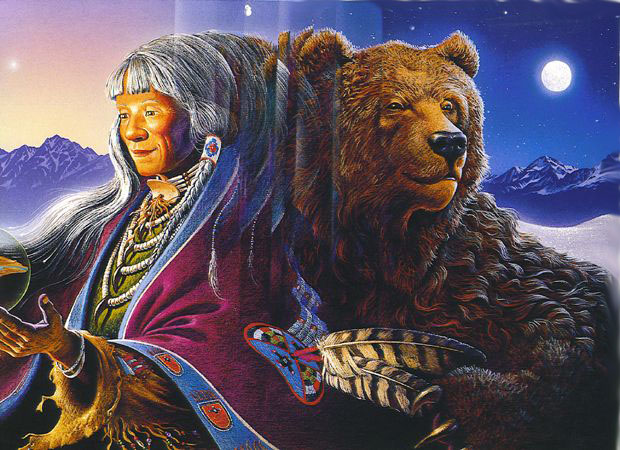

In shamanism bears are totem animals or power animals. This takes us to the very source of 'nature in motion' - the summer solstice - shaminism - the rhythm of drumming - sweat lodges and cleansing - as we meditate, initiate, and activate our DNA to uncover our lost wisdom and soul's purpose.
Patience and Connection
Hibernating with our ideas or projects until a better time presents itself. Further, bear will speak to you about connecting to both earth-based energy and celestial (sun/moon) forces. Tapping into the bear will also allow you to tap into the wax, wane and flow of life.
Confidence and Authority
By its physical presence, the bear reminds us we can be larger than life if we raise ourselves up to our inherent status. Moreover, no one questions the bear. This kind of authoritative presence will be a lesson the bear can impart.
Nurturing and Protection
We intuit these attributes by the commitment bear mothers make to their offspring. Whether your offspring is in children or ideals, the bear will lend you the determination required for rearing up strong results.
In many Native American traditions, Bear Medicine is a form of spiritual healing or guidance associated with the bear as a powerful totem or spirit animal. It is often connected to healing rituals, dream work, and personal growth, as the bear hibernates and awakens renewed - a metaphor for inner transformation. Bear Medicine might also refer to natural remedies inspired by bear behavior or plants bears are known to eat for healing purposes.
Exploring the Indigenous meanings of Bear Medicine reveals a rich, sacred, and deeply symbolic understanding rooted in the cultural, spiritual, and ecological relationships between Indigenous peoples and the natural world. While meanings vary between nations, tribes, and regions, there are some common threads across many Indigenous cultures in North America.
Bear spirit is often called upon in sweat lodge, vision quests, and medicine dances. Bear claws, fur, or teeth may be worn by healers or warriors as sacred symbols of power and protection (only with proper ceremony and respect).
Seeing a bear in a dream or vision is often a call to healing, solitude, or reclaiming personal power. A bear guide may appear during fasting and isolation periods to offer insight.
Bear items (fur, claw, representations) might be included in sacred bundles, representing the presence of Bear Spirit.
Bear Medicine is sacred, not symbolic in the Western sense. Not all teachings are shared publicly - some are oral traditions held only within the community.
If you're drawn to Bear Medicine: Spend time in quiet – like the bear in hibernation. Honor your body - bears teach healing through self-care and rest. Respect the Earth - bear reminds us to live in balance with the land. Listen to dreams - bear brings messages from the spirit world.

There is a Pawnee legend about White Bear Medicine Woman. She was born with the spirit of a bear, after her father killed a bear while she was in her mother's womb. She is the origin of the Bear Medicine Ceremony invoking healing powers by actions of a bear based on her narrative myth.
White Bear Medicine Woman is connected to the wheel/circle/completion.
Wheel of Time - Karma - Cycles of Life
The Bear Clan is a large clan of the Lower or Earth Moiety, and in contemporary Wisconsin, it is now the largest clan. The Bear Clan had to be consulted on all matters pertaining to the earth (such as land transfers), just as the Waterspirit Clan was in charge of matters pertaining to water, and the Thunderbird Clan to matters aerial. Read More...

There is evidence of prehistoric bear worship. Anthropologists such as Joseph Campbell have regarded this as a common feature in most of the fishing and hunting-tribes. The prehistoric Finns, along with most Siberian peoples, considered the bear as the spirit of one's forefathers. This is why the bear (karhu) was a greatly respected animal, with several euphemistic names (such as otso, mesikammen and kontio). The bear is the national animal of Finland.
This kind of attitude is reflected in the traditional Russian fairy tale "Morozko", whose arrogant protagonist Ivan tries to kill a mother bear and her cubs - and is punished and humbled by having his own head turned magically into a bear's head and being subsequently shunned by human society.
"The Brown Bear of Norway" is a Scottish fairy tale telling the adventures of a girl who married a prince magically turned into a bear, and who managed to get him back into a human form by the force of her love and after many trials and difficulties. In the 1970s, this story was adapted into the East German fantasy film The Singing Ringing Tree and broadcast on British television.
Evidence of bear worship has been found in early Chinese and Ainu cultures, as well (see Iomante). Korean people in their mythology identify the bear as their ancestor and symbolic animal. According to the Korean legend, a god imposed a difficult test on a she-bear; when she passed it, the god turned her into a woman and married her.
Legends of saints taming bears are common in the Alpine zone. In the arms of the bishopric of Freising, the bear is the dangerous totem animal tamed by St. Corbinian and made to carry his civilised baggage over the mountains. A bear also features prominently in the legend of St. Romedius, who is also said to have tamed one of these animals and had the same bear carry him from his hermitage in the mountains to the city of Trento.
Similar stories are told of Saint Gall and Saint Columbanus.
This recurrent motif was used by the Church as a symbol of the victory of Christianity over paganism.[59] In the Norse settlements of northern England during the 10th century, a type of "hogback" grave cover of a long narrow block of stone, with a shaped apex like the roof beam of a long house, is carved with a muzzled, thus Christianised, bear clasping each gable end. Though the best collection of these is in the church at Brompton, North Yorkshire,[60] their distribution ranges across northern England and southern Scotland, with a scattered few in the north Midlands and single survivals in Wales, Cornwall, and Ireland; a late group is found in the Orkney Islands.
Bears are a popular feature of many children's stories, including Goldilocks and "The Story of the Three Bears", the Berenstain Bears, and Winnie the Pooh.
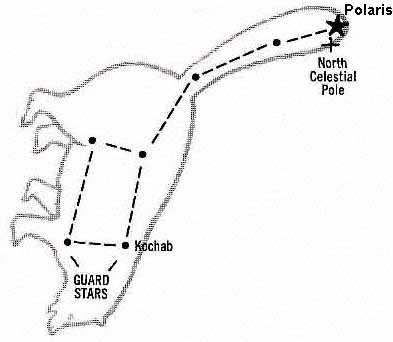
Ursa Major (Latin: "Larger She-Bear"; also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wai) is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can be seen best in the month of April. It is dominated by the widely recognized asterism known as the 'Big Dipper', 'The Wagon' and 'The Plough', which is a useful pointer towards the north, and it has mythological significance in numerous world cultures.

Ursa Major is a constellation visible throughout the year in the northern hemisphere. Its name means Great Bear in Latin, and is associated with the legend of Callisto.
Big Dipper Stars in Summer Sky Space.com - June 10, 2005
Myth: Zeus fell in love with a mortal woman named Callisto, who was a far-traveler and a huntress. His wife Hera became jealous, and changed Callisto into a large bear. When Callisto failed to return after a long journey, her son Arcas set out to find her, and in a forest one day met a huge bear. To his horror, the bear started to run toward him. Not perceiving it was his mother, Arcas fitted an arrow to his bow and was about to slay the bear, when Zeus, to avert the impending tragedy, changed Arcas into a smaller bear. Zeus could not undo Hera's spell. Then Zeus grabbed both bears by the tails, swung them around (thus stretching their tails out), and hurled them into the sky where they would be safe and immortal. However, Hera had the last word, moving them to the portion of the sky that never sets, so that until the end of the world Callisto and Arcas must endure weariness without rest.
The seven brightest stars of Ursa Major form a famous asterism known in the United Kingdom as the Plough, and was formerly called by the old name Charles's Wain ("wain" meaning "wagon") as it still is in Scandinavia, Karlavagnen. This common Germanic name originally meant the men's wagon (churls' wagon) in contrast to the women's wagon (Ursa Minor). There is also a theory that it was named after Charlemagne. In North America it is commonly known as the Big Dipper, because the major stars can be seen to follow the rough outline of a large ladle, or dipper; this is recognized as a grouping of stars in many cultures throughout the eras. In Hindu astronomy, it is referred to as Sapta Rishi meaning "The Seven Sages". Read More ...

Due to environmental changes, bears, as well as other forest animals often find food scarce. Their food sources become displaced as housing expands. As a result, many bears wander into people's yards and homes. This is an increasing pattern - as reported by friends, clients, and the media. Learning how to cope with this situation is most important so as not to endanger local residents and their pets. Here in NY state, many friends have found hungry bears lurking on their property, rummaging through garbage.

Fat Bear Week ~ Online Voting ~ Wikipedia
Fat Bear Week is an annual event held in late September or early October by Katmai National Park and Preserve in Alaska, commemorating the seasonal preparations made by Alaska peninsula brown bears inhabiting Katmai as they ready themselves for their winter hibernation.
The competition is organized by the National Park Service and Explore.org. Spectators from around the world are invited to cast online votes to determine the bear that has most effectively accumulated fat reserves. Read more ...
