
Intentional mummification in pre-Columbian Mexico was practiced by the Aztec culture. These bodies are collectively known as Aztec mummies. Genuine Aztec mummies were "bundled" in a woven wrap and often had their faces covered by a ceremonial mask. Public knowledge of Aztec mummies increased due to traveling exhibits and museums in the 19th and 20th centuries, though these bodies were typically naturally desiccated remains and not actually the mummies associated with Aztec culture. (See: Aztec mummy)
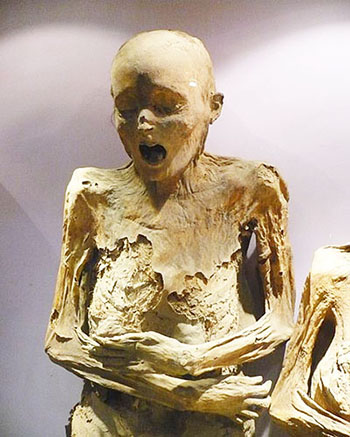
Natural mummification has been known to occur in several places in Mexico, though the most famous are the mummies of Guanajuato. A collection of these mummies, most of which date to the late 19th century, have been on display at El Museo de las Momias in the city of Guanajuato since 1970. The museum claims to have the smallest mummy in the world on display (a mummified fetus). It was thought that minerals in the soil had the preserving effect, however it may rather be due to the warm, arid climate. Mexican mummies are also on display in the small town of Encarnacion de D’az, Jalisco.
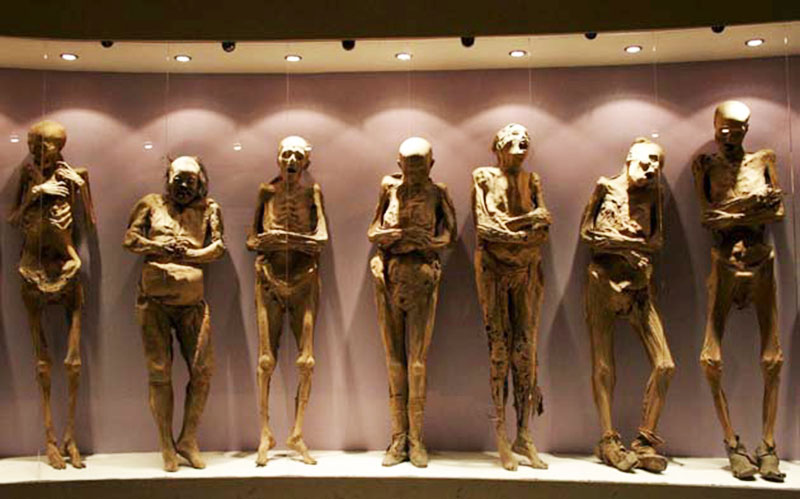

The Mummies of Guanajuato are a number of naturally mummified bodies interred during a cholera outbreak around Guanajuato, Mexico in 1833. The mummies were discovered in a cemetery in Guanajuato, making the city one of the biggest tourist attractions in Mexico.
The bodies appear to have been disinterred between 1865 and 1958. During that time a local tax was imposed requiring relatives to pay a fee to keep their relatives interred. If the relatives were unable or unwilling to pay the tax, the bodies were disinterred. Ninety percent of the remains were disinterred because their relatives did not pay the tax. Of these, only two percent had been naturally mummified. The mummified bodies were stored in a building and in the 1900s began attracting tourists. Cemetery workers began charging people a few pesos to enter the building where bones and mummies were stored. This place was turned into a museum called El Museo De Las Momias ("The Mummies' Museum"). A law prohibiting disinterring was passed in 1958, but this museum still exhibits the original mummies.