
�Carthage refers both to an ancient city in Tunisia and to the civilization that developed within the city's sphere of influence. The city of Carthage is located on the eastern side of Lake Tunis across from the center of Tunis. According to legend it was founded by Phoenician colonists under the leadership of Elissa (Queen Dido). It became a large and rich city and thus a major power of the Mediterranean until its destruction in the Third Punic War in 146 BC. Although the center of the Punic culture was destroyed, it continued into Roman times. Rome also refounded Carthage, which became one of the three most important cities of the Empire, a position that would last until the Muslim conquest when it was destroyed a second time in 698. Today Carthage is being resettled as a suburb of Tunis.
The historical study of Carthage is problematic. Because its culture and records were destroyed by the Romans at the end of the Third Punic War, very few Carthaginian primary historical sources survive. There are a few ancient translations of Punic texts into Greek and Latin, as well as inscriptions on monuments and buildings discovered in North Africa. However, the main sources are Greek and Roman historians, including Livy, Polybius, Appian, Cornelius Nepos, Silius Italicus, Plutarch, Dio Cassius, and Herodotus.
The cultures of these authors were in competition and often in conflict with Carthage. Greek cities contested with Carthage for Sicily, and the Romans fought three Punic Wars against Carthage. Inevitably, accounts of Carthage by outsiders include significant bias.
Recent excavation has brought much more primary material to light. Some of these finds contradict or confirm aspects of the traditional picture of Carthage, but much of the material is still ambiguous.
In approximately 814 BC, Carthage was founded by Phoenician settlers from the city of Tyre, bringing with them the city-god Melqart. Traditionally, the city was founded by Dido, and a number of foundation myths have survived through Greek and Roman literature.
Carthage's early years were defined by a long rivalry between the landholding and maritime families. In general, due to the city's dependence on maritime trade, the maritime faction controlled the government, and during the 6th century BC, Carthage began to acquire dominance over the Western Mediterranean. Merchants and explorers established a vast network of trade, bringing wealth and power to the city-state.
In the early 6th century BC, Hanno the Navigator is supposed to have sailed down the African coast as far as Nigeria. Meanwhile, under a leader named Malchus, the city began a systematic conquest of both the African interior and the coastal lands.
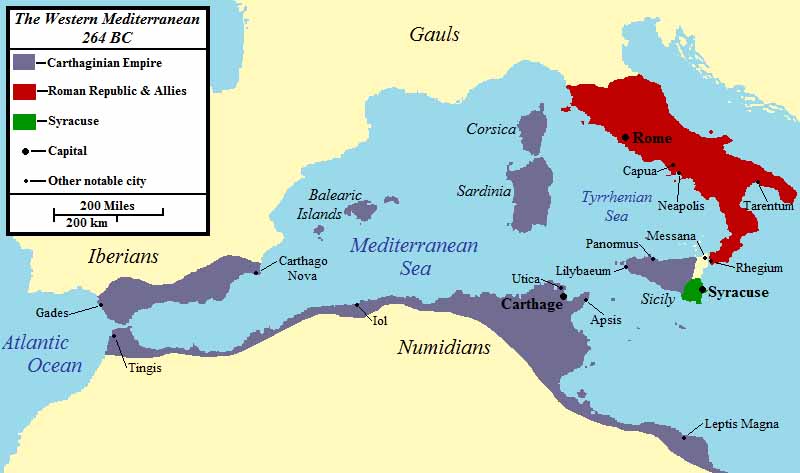
In 509 BC a treaty was signed between Carthage and Rome indicating a division of influence and commercial activities. It is the first known source that indicated Carthage had gained control over Sicily and Sardinia.
By the beginning of the 5th century BC, Carthage was the commercial center of the region, a position it would retain until overthrown by the Roman Republic. The city had conquered the territory of the old Phoenician colonies, such as Hadrumetum, Utica and Kerkouane, and the Libyan tribes, spreading its control along the North African coast from modern Morocco to the borders of Egypt. Its influence had also spread into the Mediterranean, with control over Sardinia, Malta, the Balearic Islands and the western half of Sicily. Colonies had also been established in Iberia.
The early trading empire of Carthage depended heavily on its trade with Tartessos and other cities of the Iberian peninsula, from which it obtained vast quantities of silver and, even more importantly, tin ore, which was essential to the manufacture of bronze objects by the civilizations of antiquity. Carthage followed trade routes already established by her parent city, Tyre. When Tartessos fell, the Carthaginian ships went directly to the primary sources of tin in the northwestern section of the Iberian peninsula and further north, in Cornwall in the British Isles. Other Carthaginian ships went down the Atlantic coast of Africa and brought back gold from Senegal. One account has a Carthaginian trading vessel exploring Nigeria, including identification of distinguishing geographic features, such as a coastal volcano and an encounter with gorillas. Non-permanent trade relations were established as far west as Madeira and the Canary Islands, and as far south as southern Africa.
If the epic poetry of Greece and the contemporary historians of imperial Rome record the military opposition of Carthage to the forces of the Greek city states, and later to Rome, then it is very much to the Greek theatre and Greek comedies that we are indebted for depictions of the generic Carthaginian merchant, hawking cloth, pots and jewelry. He was usually portrayed as an amusing scoundrel, a relatively peaceful and colorful trader intent on making a profit and cheating noble but innocent Greeks of every spare penny they might have. Diggings show evidence of all kinds of exchanges, from the vast quantities of tin needed for a bronze-based metals civilization to all manner of textiles, ceramics and fine metalwork. Before and in between the wars Carthaginian merchants were in every port in the Mediterranean, buying and selling, establishing warehouses where they could, or just bargaining in open-air markets after getting off their ship.
The Etruscan language has not yet been deciphered, but archaeological excavations of Etruscan cities show that the Etruscan civilization was for several centuries a customer and a vendor to Carthage, long before the rise of Rome. The Etruscan city-states were, at times, both commercial partners of Carthage and military allies.
�The government of Carthage was an oligarchal republic, which relied on a system of checks and balances and ensured a form of public accountability. The Carthaginian heads of state were called Suffets meaning "judges" and obviously related to the Biblical Hebrew ruler title Shophet "Judge"). Greek and Roman authors more commonly referred to them as "kings".
In the historically attested period, the two Suffets were elected annually from among the most wealthy and influential families and ruled collegially, similarly to Roman consuls (and equated with these by Livy). This practice might have descended from the plutocratic oligarchies that limited the Suffet's power in the first Phoenician cities.
The aristocratic families were represented in a supreme council (Roman sources speak of a Carthaginian "Senate", and Greek ones of a "council of Elders" or a gerousia), which had a wide range of powers. However, it is not known whether the Suffets were elected by this council or by an assembly of the people. Suffets appear to have exercised judicial and executive power, but not military.
Although the city's administration was firmly controlled by oligarchs, democratic elements were to be found as well: Carthage had elected legislators, trade unions and town meetings. Aristotle reported in his Politics that unless the Suffets and the Council reached a unanimous decision, the Carthaginian popular assembly had the decisive vote - unlike the situation in Greek states with similar constitutions such as Sparta and Crete.
Polybius, in his History book 6, also stated that at the time of the Punic Wars, the Carthaginian public held more sway over the government than the people of Rome held over theirs (a development he regarded as evidence of decline). Finally, there was a body known as the Hundred and Four, which Aristotle compared to the Spartan ephors. These were judges who oversaw the actions of generals, who could sometimes be sentenced to crucifixion.
Eratosthenes, head of the Library of Alexandria, noted that the Greeks had been wrong to describe all non-Greeks as barbarians, since the Carthaginians as well as the Romans had a constitution. Aristotle also knew and discussed the Carthaginian constitution in his Politics (Book II, Chapter 11).
During the period between the end of the First Punic War and the end of the Second Punic War, members of the Barcid family dominated in Carthaginian politics. They were given control of the Carthaginian military and all the Carthaginian territories outside of Africa.
Carthage under the Phoenicians was notorious to its neighbors for child sacrifice. Plutarch (ca. 46-120 CE) mentions the practice, as do Tertullian, Orosius and Diodorus Siculus. Livy and Polybius do not.
Modern archeological excavations could be taken to confirm Plutarch's view. In a single child cemetery called the Tophet an estimated 20,000 urns were deposited between 400 BC and 200 BC, with the practice continuing until the early years of the Christian period. The urns contained the charred bones of newborns and in some cases the bones of fetuses and 2-year-olds.
These remains have been interpreted to mean that in the cases of stillborn babies, the parents would sacrifice their youngest child. There is a clear correlation between the frequency of sacrifice and the well-being of the city. In bad times (war, poor harvests) sacrifices became more frequent, indicating an increased assiduousness in seeking divine appeasement.
It is sometimes argued, however, that these bodies were merely the cremated remains of children that died naturally, although in light of other Canaanite evidence this seems less likely. The few Carthaginian texts which have survived make absolutely no mention of child sacrifice. It has been argued by some modern scholars that evidence of Carthaginian child sacrifice is sketchy at best and that it is far more likely to have been part of Roman propaganda against the Carthaginians to justify their conquest and destruction. The debate is ongoing among modern archeologists and other antiquarians.
While the surviving Punic texts mention no practices of religious sacrifices, they are detailed enough to give a portrait of a very well organized caste of temple priests and acolytes performing different types of functions, for a variety of prices.Carthage had many gods. The supreme divine couple was that of Tanit and Ba'al Hammon. Priests were clean shaven, unlike most of the population. In the first centuries of the city ritual celebrations included rhythmic dancing, derived from Phoenician traditions.
The goddess Astarte seems to have been popular in early times. At the height of its cosmopolitan era Carthage seems to have hosted a large array of divinities from the neighboring civilizations of Greece, Egypt and the Etruscan city-states.
Carthage under the Phoenicians was notorious to its neighbors for child sacrifice. Plutarch (ca. 46-120 CE) mentions the practice, as do Tertullian, Orosius and Diodorus Siculus. Livy and Polybius do not. Modern archeological excavations could be taken to confirm Plutarch's view. In a single child cemetery called the Tophet an estimated 20,000 urns were deposited between 400 BC and 200 BC, with the practice continuing until the early years of the Christian period.
The urns contained the charred bones of newborns and in some cases the bones of fetuses and 2-year-olds. These remains have been interpreted to mean that in the cases of stillborn babies, the parents would sacrifice their youngest child. There is a clear correlation between the frequency of sacrifice and the well-being of the city. In bad times (war, poor harvests) sacrifices became more frequent, indicating an increased assiduousness in seeking divine appeasement.
It is sometimes argued, however, that these bodies were merely the cremated remains of children that died naturally, although in light of other Canaanite evidence this seems less likely. The few Carthaginian texts which have survived make absolutely no mention of child sacrifice. It has been argued by some modern scholars that evidence of Carthaginian child sacrifice is sketchy at best and that it is far more likely to have been part of Roman propaganda against the Carthaginians to justify their conquest and destruction. The debate is ongoing among modern archeologists and other antiquarians.
While the surviving Punic texts mention no practices of religious sacrifices, they are detailed enough to give a portrait of a very well organized caste of temple priests and acolytes performing different types of functions, for a variety of prices.
Carthage had many gods. The supreme divine couple was that of Tanit and Ba'al Hammon. Priests were clean shaven, unlike most of the population. In the first centuries of the city ritual celebrations included rhythmic dancing, derived from Phoenician traditions. The goddess Astarte seems to have been popular in early times. At the height of its cosmopolitan era Carthage seems to have hosted a large array of divinities from the neighboring civilizations of Greece, Egypt and the Etruscan city-states.
Carthage's success led to the creation of a powerful navy to discourage both pirates and rival nations. This, coupled with its success and growing hegemony, brought Carthage into increasing conflict with the Greeks, the other major power contending for control of the central Mediterranean.
The island of Sicily, lying at Carthage's doorstep, became the arena on which this conflict played out. From their earliest days, both the Greeks and Phoenicians had been attracted to the large island, establishing a large number of colonies and trading posts along its coasts. Small battles had been fought between these settlements for centuries.
By 480 BC, Gelon, the tyrant of Greek Syracuse, backed in part by Greek support, was attempting to unite the island under his rule. This imminent threat could not be ignored, and Carthage - possibly as part of an alliance with Persia, then engaged in a war with Greece - fielded its largest military force to date, under the leadership of the general Hamilcar. Traditional accounts give Hamilcar's army a strength of three hundred thousand men; though these are almost certainly exaggerated, it must nonetheless have been of formidable force.
En route to Sicily, however, Hamilcar suffered losses (possibly severe) due to poor weather. Landing at Panormus (modern-day Palermo), he was then decisively defeated by Gelon at the Battle of Himera. He was either killed during the battle or committed suicide in shame. The loss severely weakened Carthage, and the old government of entrenched nobility was ousted, replaced by the Carthaginian Republic.
By 410 BC Carthage had recovered under a series of successful rulers. It had conquered much of modern day Tunisia, strengthened and founded new colonies in North Africa, and sponsored Mago Barca's journey across the Sahara Desert and Hanno the Navigator's journey down the African coast.
Although, in that year, the Iberian colonies seceded - cutting off Carthage's major supply of silver and copper - Hannibal Mago, the grandson of Hamilcar, began preparations to reclaim Sicily, while expeditions were also led into Morocco and Senegal, and also into the Atlantic.
In 409 BC, Hannibal Mago set out for Sicily with his force. He was successful in capturing the smaller cities of Selinus (modern Selinunte) and Himera, before returning triumphantly to Carthage with the spoils of war.
But the primary enemy, Syracuse, remained untouched, and in 405 BC Hannibal Mago led a second Carthaginian expedition, this time to claim the island in its entirety.
This time, however, he met with fierce resistance and ill-fortune. During the siege of Agrigentum, the Carthaginian forces were ravaged by plague, Hannibal Mago himself succumbing to it.
Although his successor, Himilco, successfully extended the campaign by breaking a Greek siege, capturing the city of Gela and repeatedly defeating the army of Dionysius, the new tyrant of Syracuse, he, too, was weakened by the plague and forced to sue for peace before returning to Carthage.
In 398 BC, Dionysius had regained his strength and broke the peace treaty, striking at the Carthaginian stronghold of Motya.
Himilco responded decisively, leading an expedition which not only reclaimed Motya, but also captured Messina. Finally, he laid siege to Syracuse itself. The siege met with great success throughout 397 BC, but in 396 BC plague again ravaged the Carthaginian forces, and they collapsed.
Sicily by this time had become an obsession for Carthage. Over the next sixty years, Carthaginian and Greek forces engaged in a constant series of skirmishes.
By 340 BC, Carthage had been pushed entirely into the southwest corner of the island, and an uneasy peace reigned over the island.
In 315 BC Agathocles, the tyrant of Syracuse, seized the city of Messene (present-day Messina). In 311 BC he invaded the last Carthaginian holdings on Sicily, breaking the terms of the current peace treaty, and laid siege to Akragas.
Hamilcar, grandson of Hanno the Navigator, led the Carthaginian response and met with tremendous success. By 310 BC he controlled almost all of Sicily and had laid siege to Syracuse itself. In desperation, Agathocles secretly led an expedition of 14,000 men to the mainland, hoping to save his rule by leading a counterstrike against Carthage itself. In this, he was successful: Carthage was forced to recall Hamilcar and most of his army from Sicily to face the new and unexpected threat. Although Agathocles' army was eventually defeated in 307 BC, Agathocles himself escaped back to Sicily and was able to negotiate a peace which maintained Syracuse as a stronghold of Greek power in Sicily.
Between 280 BC and 275 BC, Pyrrhus of Epirus waged two major campaigns in an effort to protect and extend the influence of the Greeks in the western Mediterranean: one against the emerging power of the Roman Republic to defend the Greek colonies in southern Italy, the other against Carthage in a renewed attempt to wrest Sicily wholly from their control.
After winning a complete victory over Rome at Heraclea, and another complete yet very costly victory at Asculum, Pyrrhus was soon distracted by opportunities in mainland Greece which had recently been invaded by the Gauls, and the Greeks of Sicily. Making a temporary peace with the Romans he left for Sicily and between 278-276 BC, defeated every Carthaginian force against him. Pyrrhus even managed to take Eryx, the strongest Carthaginian holdout. Yet at Lilybaeum, the Carthaginians were able to hold out against Pyrrhus, and the invader, soon found that he was no longer welcome by the Greek Sicilians. Leaving once again for Italy, he fought the Romans once more to a draw.
Not having the resources and manpower to continue, Pyrrhus left for Epirus. For Carthage, this meant a return to the status quo. For Rome, however, it meant capturing Tarentum and holding the entirety of Italy. The result was a shift in the balance of power in the western Mediterranean: the Greeks were effectively reduced to their toehold in Sicily, while Rome's growing strength and territorial ambitions brought it directly into conflict with Carthage for the first time.
When Agathocles died in 288 BC, a large company of Italian mercenaries who had previously been held in his service found themselves suddenly without employment. Rather than leave Sicily, they seized the city of Messana. Naming themselves Mamertines (or "sons of Mars"), they became a law unto themselves, terrorizing the surrounding countryside.
The Mamertines became a growing threat to Carthage and Syracuse alike. In 265 BC, Hiero II, former general of Pyrrhus and the new tyrant of Syracuse, took action against them. Faced with a vastly superior force, the Mamertines divided into two factions, one advocating surrender to Carthage, the other preferring to seek aid from Rome. As a result, embassies were sent to both cities.
While the Roman Senate debated the best course of action, the Carthaginians eagerly agreed to send a garrison to Messana. A Carthaginian garrison was admitted to the city, and a Carthaginian fleet sailed into the Messanan harbor. However, soon afterwards they began negotiating with Hiero; alarmed, the Mamertines sent another embassy to Rome asking them to expel the Carthaginians.
Her intervention had placed Carthage's military forces directly across the narrow channel of water that separated Sicily from Italy. Moreover, the presence of the Carthaginian fleet gave them effective control over this channel, the Strait of Messina, and demonstrated a clear and present danger to nearby Rome and her interests.
As a result, the Roman Assembly, although reluctant to ally with a band of mercenaries, sent an expeditionary force to return control of Messana to the Mamertines.
The Roman attack on the Carthaginian forces at Messana triggered the first of The Punic Wars. Over the course of the next century, these three major conflicts between Rome and Carthage would determine the course of Western civilization.
The Punic Wars were a series of three wars fought between Rome and the Phoenician city of Carthage. They are known as the "Punic" Wars because Rome's name for Carthaginians was Punici (older Poenici, due to their Phoenician ancestry).
The primary cause of the Punic Wars was the clash of interests between the expanding Carthaginian and Roman spheres of influence. The Romans were particularly interested in expansion via Sicily, most of which lay under Carthaginian control. At the start of the first Punic War, Carthage was the ascendant power of the Mediterranean, with an extensive maritime empire, while Rome was rapidly rising in prominence as the dominant power in Italy. By the conclusion of the third war, Rome had conquered Carthage's entire empire and razed the city itself to the ground, becoming in the process the most powerful state of the Mediterranean.
The Second Punic War (218 BC to 201 BC) - is famous for Hannibal's crossing of the Alps. Hannibal invaded Italy and defeated the Roman army in several battles, but never managed to effect a political break between Rome and her allies. Hispania, Sicily and Greece were also key theatres, Rome emerging victorious in all three. Eventually, the war was taken to Africa and Carthage defeated, being reduced to the city itself and losing all power.
The Third Punic War (149 BC to 146 BC) - was the three year siege of Carthage, ending in that city's destruction.
Rome consistently triumphed over Carthage during the Punic Wars. The end of the Third Punic War resulted in the end of Carthaginian power and the complete destruction of the city by Scipio Aemilianus: Roman soldiers went from house to house, slaughtering the people of Carthage and enslaving any who survived. Carthage's harbor was burned and the city razed.
Between the first and the second Punic war, Carthage faced a major mercenary revolt. During the mercenary revolt Rome was able to acquire Sardinia.
Between the first and the second Punic war, Carthage faced a major mercenary revolt. During the mercenary revolt Rome was able to acquire Sardinia.
It is disputed whether the Carthaginian farmland was salted following the Battle of Carthage.
The site was too well-chosen to let it go to waste, however, and a new city grew up there, eventually becoming the second largest city in the western half of the Roman empire. By the late 2nd century, Carthage was the center of the Roman province of Africa, with a population of over 400,000 people. It briefly became the capital of an usurper, Domitius Alexander, in 308-311.
Carthage also became a centre of early Christianity. Tertullian rhetorically addresses the Roman governor with the fact that the Christians of Carthage that just yesterday were few in number, now "have filled every place among you - cities, islands, fortresses, towns, market-places, the very camp, tribes, companies, palaces, senate, forum; we have left nothing to you but the temples of your gods." (Apologeticus written at Carthage, c. 197.) It is worth noting that Tertullian omits any mention of the surrounding countryside or its network of villas not unlike colonial hacienda society.
In the first of a string of rather poorly reported Councils at Carthage a few years later, no fewer than seventy bishops attended. Tertullian later broke with the mainstream that was represented more and more by the bishop of Rome, but a more serious rift among Christians was the Donatist controversy, which drew in the young Augustine of Hippo while he finished his education at Carthage before moving on to Rome. In 397 at the Council at Carthage, the Biblical canon for the western Church was confirmed.
The political fallout from the deep disaffection of African Christians was a crucial factor in the ease with which Carthage and the other centres were captured in the 5th century by Gaiseric, king of the Vandals, who defeated the Byzantine general Bonifacius and made the city his capital. Gaiseric was considered a heretic too, an Arian, and though Arians commonly despised Catholic Christians, a mere promise of toleration might have caused the city's population to accept him. After a failed attempt to recapture the city in the 5th century, the Byzantines finally subdued the Vandals in the 6th century. Using Gaiseric's grandson's deposal by a distant cousin, Gelimer, as a pretext, the Byzantines dispatched an army to conquer the Vandal kingdom. On Sunday, October 15, 533, the Byzantine general Belisarius, accompanied by his wife Antonina, made his formal entry into Carthage, sparing it a sack and a massacre.
During the emperor Maurice's reign, Carthage was made into an Exarchate, as was Ravenna in Italy. These two exarchates were the western bulwarks of Byzantium, all that remained of its power in the west. In the early 7th century, it was the Exarch of Carthage, Heraclius (of Armenian origin), who overthrew Emperor Phocas.
The Byzantine Exarchate was not, however, able to withstand the Arab conquerors of the 7th century. The first Arab assault on the Exarchate of Carthage was initiated from Egypt without much success in 647. A more protracted campaign lasted from 670-683. In 698 the Exarchate of Africa was finally overrun by the rising forces of Islam. Read more
ANCIENT AND LOST CIVILIZATIONS